Interfacing DHT11 Temperature and Humidity Sensor with STM32 Using HAL
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to interface the DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor with an STM32 microcontroller using HAL libraries.
The DHT11 is a popular digital sensor used in weather monitoring and home automation projects. We’ll cover the wiring, initialization sequence, and how to read sensor data accurately using precise timing with STM32 timers. Whether you’re working with STM32F1, STM32F4, or other variants, this guide provides complete code examples and explanations to help you get started quickly.
prerequisites:
- We have already covered how to generate the delay in microseconds using timer in STM32. Today we will utilize the delay in microseconds to interface the DHT22 temperature and Humidity sensor with STM32.
- You can also check out the similar tutorials covering how to interface the DHT22 sensor with STM32 and Interface DS18B20 sensor with STM32.
- We will display the results on LCD16x2, which is connected via the I2C. You can check the tutorial Interface the LCD via I2C with STM32.
If you are not able to get DHT11 or DHT22 values, Here is another method you can use. This one is unified for both the sensors. No setup needed for timer and all. Just select the data pin as output and you are done. you need to configure the DHT TYPE in DHT.c file. Download it from https://controllerstech.com/wp-content
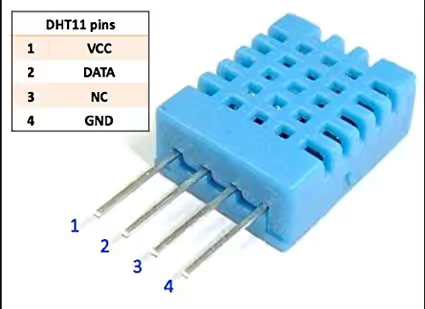
Introducing DHT11 Temperature & Humidity Sensor
The DHT11 is a low-cost digital sensor that measures both temperature and humidity. It’s widely used in DIY electronics, weather stations, and home automation projects. The sensor provides calibrated digital output and communicates with microcontrollers using a single-wire protocol, making it easy to interface with platforms like STM32.
Key Features of DHT11:
- Measures Temperature and Humidity – Provides reliable readings with decent accuracy for most applications.
- Single-Wire Digital Interface – Requires only one data pin for communication.
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V to 5V – Compatible with both 3.3V and 5V logic systems.
- Compact and Low Power – Ideal for battery-operated and space-constrained designs.
Why should you choose DHT11 Sensor over others?
The DHT11 is a great choice for beginners and hobby projects due to its simplicity, affordability, and ease of use. It offers digital output, so no complex ADC conversion is required, and it only needs one GPIO pin for communication. The sensor is ideal for basic temperature and humidity monitoring where high accuracy is not critical. Its wide voltage compatibility (3.3V–5V) also makes it suitable for most microcontrollers, including STM32 boards.
DHT11 vs DHT22 which one is better ?
The table below shows the comparison between the DHT11 an DHT22.
| Feature | DHT11 | DHT22 |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | 0°C to 50°C | -40°C to +80°C |
| Temperature Accuracy | ±2°C | ±0.5°C |
| Humidity Range | 20% to 90% RH | 0% to 100% RH |
| Humidity Accuracy | ±5% RH | ±2–5% RH |
| Sampling Rate | 1 reading per second (1Hz) | 0.5 reading per second (2s interval) |
| Operating Voltage | 3.3V to 5V | 3.3V to 6V |
| Data Format | Digital (1-wire) | Digital (1-wire) |
| Cost | Lower cost | Slightly higher |
| Size | Smaller | Slightly larger |
| Use Case | Basic hobby projects | Projects needing better accuracy |
The choice is simple:
- Choose DHT11 for budget-friendly, basic monitoring.
- Choose DHT22 when you need better accuracy, wider range, and more reliability.
How does the DHT11 Communicate ?
The DHT11 uses one wire to communicate to the MCU. Therefore it is a very time sensitive device. Below are the timing diagrams from the DHT11 datasheet, used in different processes.
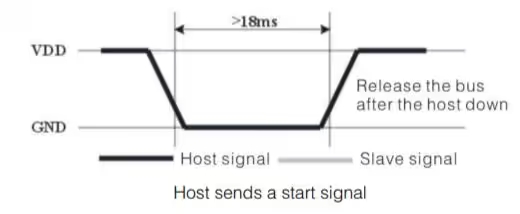
Initialization
The DHT11 initialization starts with the microcontroller pulling the data line LOW for 18 ms, then switching it to input mode. The sensor responds by pulling the line LOW for 80 µs, then HIGH for 80 µs, signaling it’s ready to send data.
Below the image shows the START condition.
- As shown above, in order to initialise the sensor, we have to first pull the data line LOW for around 18 ms.
- After this DHT11 will pull the line LOW for 80 us ,and than HIGH for 80 us.
- Once this is done, the sensor will be initialized and start transmitting
Below are the Steps for Generating the Start for DHT11 sensor.
- Set the pin (data) as output
- Pull the pin low for 18ms
- Release the pin by setting it as input
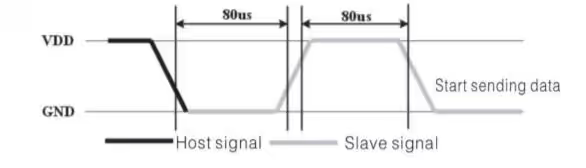
DHT11 will now send the response as you can see in the figure above.
In order to indicate it’s presence, after receiving the start signal, DHT11 will send a response signal. To do so, it will pull the data line low for 80 us, and than high for another 80 us. To read this response, we will do the following
- Wait for 40 us.
- Read the pin, it must be low at this point.
- Wait for 80 us.
- Read the pin, this time it should be HIGH.
If the above conditions are satisfied, that means the sensor is present, and we can proceed with reading the data.
DATA Transmission
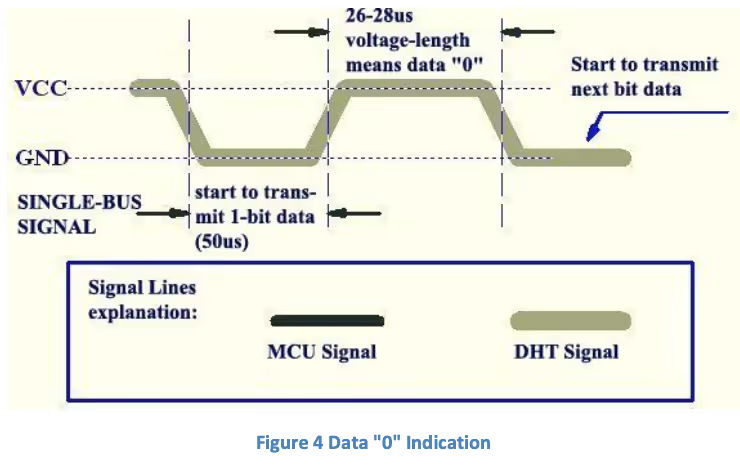
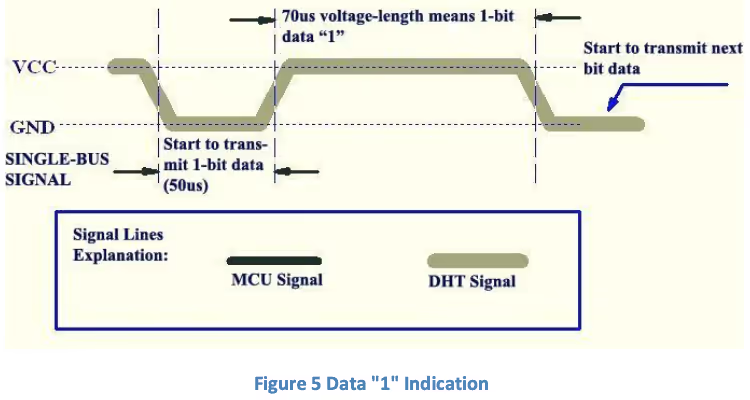
During data transmission, the DHT11 sends 40 bits of data after the initialization. Each bit starts with a 50 µs LOW pulse, followed by a HIGH pulse. The duration of the HIGH pulse determines the bit: around 26–28 µs for a ‘0’ and around 70 µs for a ‘1’. These 40 bits include humidity, temperature, and a checksum byte.
The 40 bits sent by DHT11 are as follows :
DATA = 8 bit integral RH data + 8 bit decimal RH data + 8 bit integral T data+8 bit decimal T data + 8 bit checksum
If the data transmission is right, check-sum should be the last 8 bit of “8 bit integral RH data+8 bit decimal RH data+8 bit integral T data+8 bit decimal T data”
Following are the steps to READ DATA from the sensor:
- Wait for the pin to go high.
- Wait for 40us. This is because the length of “0” bit is 26-28us, and if the pin is high after 40us, it indicates that the bit is “1”.
- write the respective values to the variable.
Wiring Diagram
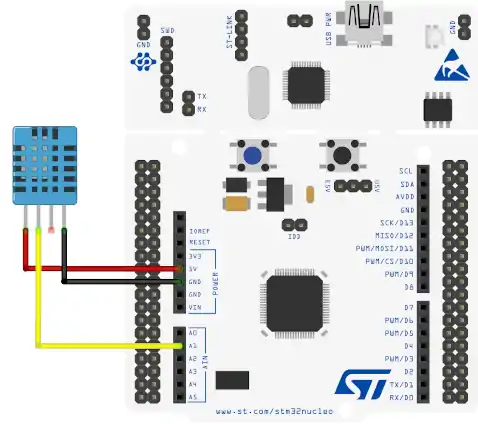
Below is the image showing the connection between DHT22 and STM32 Nucleo-F446.
Since the DHT11 only uses 1 wire to communicate to the MCU, I have connected it to the pin PA1. The sensor is powered with 3.3V from the nucleo board itself.
The LCD1602 is connected via PCF8574 using the I2C. The connection with the STM32 is shown in the table below.
| PCF8574 Pin | STM32F103 Pin | Description |
|---|---|---|
| VCC | 5V | Power supply (5V) |
| GND | GND | Ground |
| SDA | PB7 | I²C Data line |
| SCL | PB6 | I²C Clock line |
STM32CubeMX Configuration
Clock Configuration
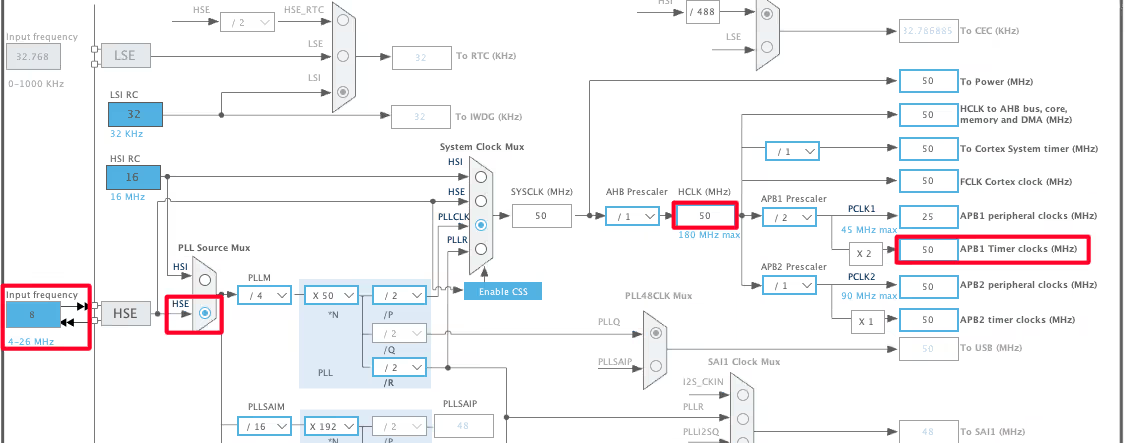
Below is the image showing the clock configuration for this project.
The system is clocked from the external 8MHz crystal and the HCLK is set to 50MHz.
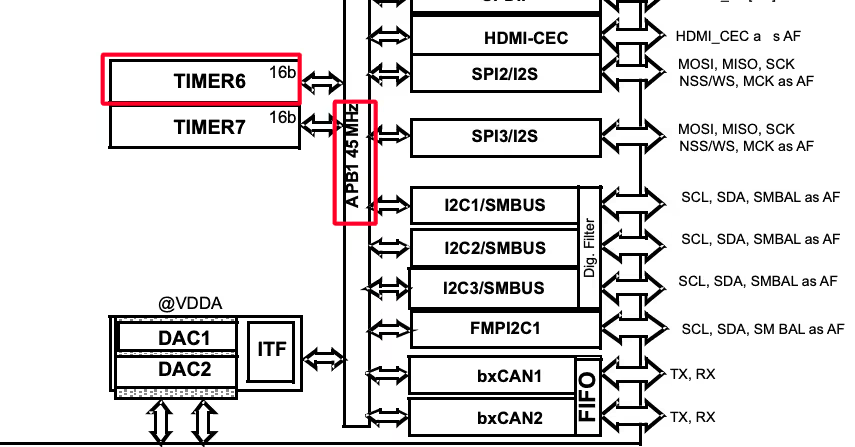
Note that the APB1 Timer clock is also at 50MHz. This is important because we will use the TIM6 to generate the delays in microseconds and the TIM6 is connected to the APB1 bus.
Timer Configuration
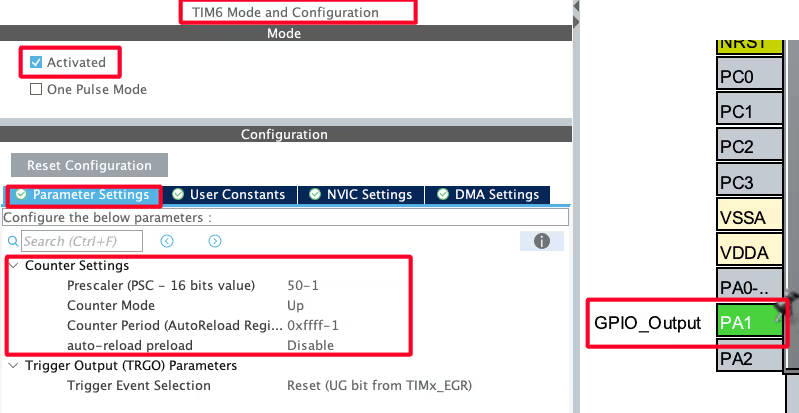
Below is the image showing the configuration of the TIM6.
Since the APB1 Timer clock is at 50MHz, we will use the prescaler of 50 to bring the TIM6 clock to 1 MHz. This is already explained in the tutorial which explains how to generate the delays in microseconds.
The pin PA1 is set as output, this is where the DHT11 data pin is connected to.
I2C Configuration for LCD1602
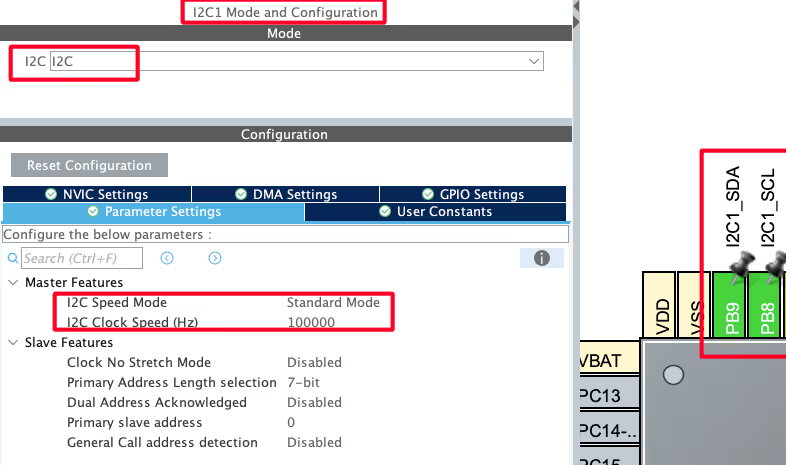
I am using the LCD16x2 to display the Temperature and Humidity data. The LCD is connected using the PCF8574 I2C extender. Below is the image showing the I2C configuration.
I am using the I2C1 to connect the LCD. The I2C is configured in the standard mode with the clock speed set to 100KHz. The pins PB8 and PB9 are configured as the SCL and SDA pins.
We have already covered how to Interface the LCD via I2C with STM32. You can check out the tutorial for more details.
HAL-Based Code for DHT22 Communication
Initialization
As explained in the Initialization section, below is the code for the same.
void DHT11_Start (void)
{
Set_Pin_Output (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN); // set the pin as output
HAL_GPIO_WritePin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN, 0); // pull the pin low
delay (18000); // wait for 18ms
Set_Pin_Input(DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN); // set as input
}- Set the pin (data) as output.
- Pull the pin low and wait for 18ms.
- set the pin as input for receiving the data.
Response
We will check the response sent by the DHT11 sensor.
uint8_t Check_Response (void)
{
uint8_t Response = 0;
delay (40);
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)))
{
delay (80);
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))) Response = 1;
else Response = -1;
}
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
return Response;
}- wait for 40 us.
- Check if the pin is low, than wait for 80 us. This will totally be a delay of 120 us and the pin should be high now.
- Check if the pin is high. If it is, than the response is OK.
Read Data
Below is the function to read the Data from the sensor.
uint8_t DHT11_Read (void)
{
uint8_t i,j;
for (j=0;j<8;j++)
{
while (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go high
delay (40); // wait for 40 us
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))) // if the pin is low
{
i&= ~(1<<(7-j)); // write 0
}
else i|= (1<<(7-j)); // if the pin is high, write 1
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
return i;
}- Wait for the pin to go high.
- Wait for 40 us. This is because the length of “0” bit is 26-28 us and if the pin is high after 40 us, it indicates that the bit is “1”.
- Write the respective values to the variable.
The main function
int main()
{
.....
HAL_TIM_Base_Start(&htim6); // for us Delay
lcd_init();
lcd_send_string("INITIALISING>>>>");
HAL_Delay(2000);
lcd_clear ();
while (1)
{
DHT11_Start();
Presence = DHT11_Check_Response();
Rh_byte1 = DHT11_Read ();
Rh_byte2 = DHT11_Read ();
Temp_byte1 = DHT11_Read ();
Temp_byte2 = DHT11_Read ();
SUM = DHT11_Read();
TEMP = Temp_byte1;
RH = Rh_byte1;
Temperature = (float) TEMP;
Humidity = (float) RH;
HAL_Delay(3000);
}
}- We will first send the START condition an then check for the Presence.
- The read the 40 bit data in sequence and store it in the 5 bytes.
- Then combine the Temperature data together and Humidity data together.
- To get the actual data in °C and %Rh, we just need to Read the 1st byte of the Temp and RH data. The DHT11 does not send the decimal data, so 2nd bytes are irrelevant.
- Finally Display the data on the LCD.
Since we are also displaying the data on the LCD, the LCD is initialized in the main function itself. We have already covered how to use the LCD1602 via I2C to display strings, numbers, floats etc. Below are the functions for displaying the data on the LCD.
void Display_Temp (float Temp)
{
char str[20] = {0};
lcd_put_cur(0, 0);
sprintf (str, "TEMP:- %.2f ", Temp);
lcd_send_string(str);
lcd_send_data('C');
}void Display_Rh (float Rh)
{
char str[20] = {0};
lcd_put_cur(1, 0);
sprintf (str, "RH:- %.2f ", Rh);
lcd_send_string(str);
lcd_send_data('%');
}Result on the LCD1602
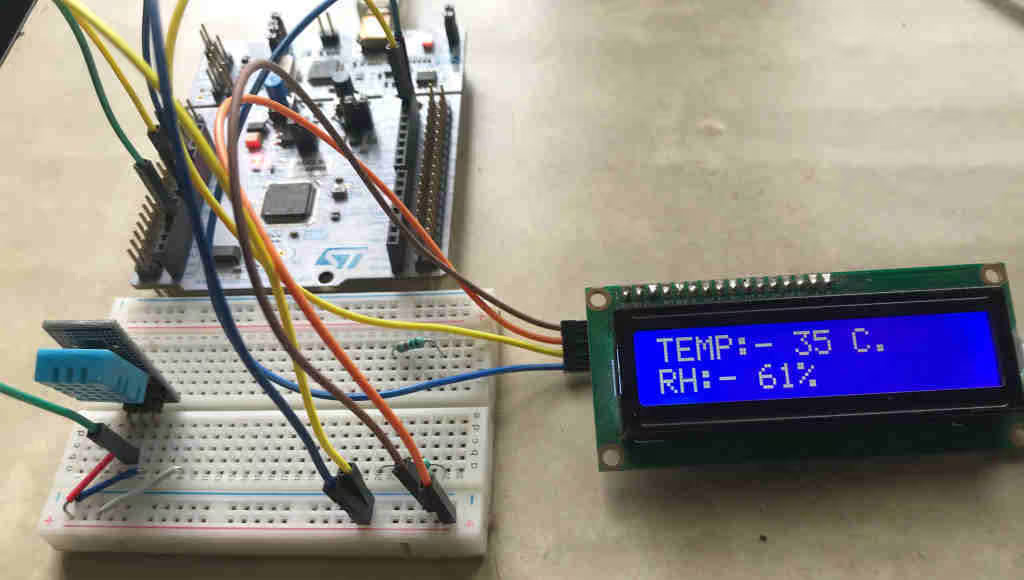
The image below shows the final output on the LCD display:
As you can see, the temperature and humidity (RH) values are successfully displayed on the LCD. In this example, the temperature is shown as 35°C and the relative humidity as 61%.
VIDEO TUTORIAL
STM32 DHT11 Temperature & Humidity Tutorial Video
This tutorial demonstrates how to interface the DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor with an STM32 microcontroller using STM32CubeIDE and HAL libraries. You’ll learn how the DHT11 communication works, how to generate precise microsecond delays using a timer, send the start signal to the sensor, read the 40-bit data packet, and extract temperature and humidity values accurately. To make it easier to follow, a video walkthrough is included showing the full process in action. Follow the written guide alongside the video for complete understanding.
Watch the VideoConclusion
In this tutorial, we successfully interfaced the DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor with an STM32 microcontroller using HAL libraries and timer-based delays. We covered the complete setup, including CubeMX configuration, initialization and data reading sequence, and LCD display output. The DHT11 sensor is ideal for basic weather or environmental monitoring projects due to its simplicity and low cost.
You can check out interfacing similar sensors like DHT22 sensor with STM32 and DS18B20 sensor with STM32.
Checkout More STM32 Sensors Tutorials
How to Interface SHT21 Sensor with STM32 using I2C (Step-by-Step with Code and Circuit Diagram)
How to interface MPU6050 (GY-521) with STM32
Multiple DS18B20 sensors using UART
Interface BMP180 with STM32
STM32 DHT22 Temperature & Humidity Sensor with HAL
Interfacing ADXL345 Accelerometer with STM32 via I2C
GP2Y0A41SK0F STM32 ADC Distance Measurement Guide
STM32 DHT11 Project Download
Info
You can help with the development by DONATING Below.
To download the project, click the DOWNLOAD button.
STM32 DHT11 FAQs
Yes, the DHT11 can be used with any STM32 microcontroller, as long as you have access to a GPIO pin and a timer to generate microsecond delays.
The DHT11 communicates using strict timing requirements at the microsecond level. Accurate microsecond delays are essential for detecting sensor response and reading each bit correctly.
Ensure your microsecond delay function is accurate, the pull-up resistor is connected properly, and there’s enough delay (at least 2–3 seconds) between each read attempt.
No, DHT22 has a different data format and higher resolution. Although the interfacing method is similar, the code needs to be modified to work with DHT22.
The DHT11 should be read no more than once every 2 seconds to ensure reliable data. Reading it too frequently may return the same data or cause communication errors.




Is it possible to do it without using hal library.
Yes of course. The only modification you need to do is for delay and reading and writing pins. All of these are already explained in the Register based tutorial series.
That’s a very well written and clean library. Runs like a charm on my STM32F401RE Nucleo board and helps me a lot with debugging my own code – thank you!
Hello, thank you very much for your tutorial.
It will not work on STM32F103C8 unless you rewrite “delay” function. After that it will work ok.
i have problem when i put lcd_init() in main DTH not work ,but when i delete it DHT work probably
Hi
I have a problem with Delay microseconds, use STM32F103C8. It isn’t correct as I setup
Hi
my code gets stuck when go in the function DHT11_Check_Response in the “While (((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)));”
can you look my code? :/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* <h2><center>© Copyright (c) 2020 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.</center></h2>
*
* This software component is licensed by ST under BSD 3-Clause license,
* the “License”; You may not use this file except in compliance with the
* License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
* opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ——————————————————————*/
#include “main.h”
/* Private includes ———————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
//#include “i2c-lcd.h”
#include “stdio.h”
#include <stdlib.h>
#include “math.h”
#include “stdint.h”
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef ———————————————————–*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ————————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro ————————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ———————————————————*/
I2C_HandleTypeDef hi2c1;
TIM_HandleTypeDef htim6;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart2;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes ———————————————–*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void);
static void MX_TIM6_Init(void);
static void MX_I2C1_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTORYPE int fputc (int ch, FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE
{
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xFFFF);
return ch;
}
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ———————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
void delay (uint16_t time)
{
/* change your code here for the delay in microseconds */
__HAL_TIM_SET_COUNTER(&htim6, 0);
while ((__HAL_TIM_GET_COUNTER(&htim6))<time);
}
void Display_Temp (float Temp)
{
char str[20] = {0};
//lcd_put_cur(0, 0);
uint8_t tempaux[]=”hola”;
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart2, tempaux, sizeof(tempaux), 1000);
sprintf(str,”TEMP:- %.2f “, Temp);
//lcd_send_string(str);
//lcd_send_data(‘C’);
}
void Display_Rh (float Rh)
{
char str[20] = {0};
//lcd_put_cur(1, 0);
sprintf (str, “RH:- %.2f “, Rh);
//lcd_send_string(str);
//lcd_send_data(‘%’);
}
uint8_t Rh_byte1, Rh_byte2, Temp_byte1, Temp_byte2;
uint16_t SUM, RH, TEMP;
float Temperature = 0;
float Humidity = 0;
uint8_t Presence = 0;
void Set_Pin_Output (GPIO_TypeDef *GPIOx, uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOx, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void Set_Pin_Input (GPIO_TypeDef *GPIOx, uint16_t GPIO_Pin)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOx, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/*********************************** DHT11 FUNCTIONS ********************************************/
#define DHT11_PORT GPIOA
#define DHT11_PIN GPIO_PIN_1
void DHT11_Start (void)
{
Set_Pin_Output(DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN);
/* Nivel de comienzo de comunicación */
delay(1000);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN, 0);
delay (18000);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN, 1);
delay(20);
Set_Pin_Input(DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN);
}
uint8_t DHT11_Check_Response (void)
{
uint8_t Response = 0;
delay (40);
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)))
{
delay (80);
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))) Response = 1;
else Response = -1; // 255
}
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
return Response;
}
uint8_t DHT11_Read (void)
{
uint8_t i,j;
for (j=0;j<8;j++)
{
while (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go high
delay (40); // wait for 40 us
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))) // if the pin is low
{
i&= ~(1<<(7-j)); // write 0
}
else i|= (1<<(7-j)); // if the pin is high, write 1
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
return i;
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration——————————————————–*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
MX_TIM6_Init();
MX_I2C1_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_TIM_Base_Start(&htim6);
// lcd_init();
// lcd_send_string(“INITIALISING>>>>”);
// HAL_Delay(2000);
// lcd_clear ();
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
// Display_Temp(Temperature);
// Display_Rh(Humidity);
/********************** DHT11 *********************/
Display_Temp(Temperature);
Display_Rh(RH);
DHT11_Start();
Presence = DHT11_Check_Response();
Rh_byte1 = DHT11_Read ();
Rh_byte2 = DHT11_Read ();
Temp_byte1 = DHT11_Read ();
Temp_byte2 = DHT11_Read ();
SUM = DHT11_Read();
TEMP = Temp_byte1;
RH = Rh_byte1;
Temperature = (float) TEMP;
Humidity = (float) RH;
// Display_Temp(Temperature);
printf(“, %f\n\r*”,Temperature);
printf(“, %f\n\r*”,Humidity);
HAL_Delay(3000);
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
RCC_PeriphCLKInitTypeDef PeriphClkInit = {0};
/** Initializes the RCC Oscillators according to the specified parameters
* in the RCC_OscInitTypeDef structure.
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSI|RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEPredivValue = RCC_HSE_PREDIV_DIV1;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSIState = RCC_HSI_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSICalibrationValue = RCC_HSICALIBRATION_DEFAULT;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLMUL = RCC_PLL_MUL9;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB buses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
PeriphClkInit.PeriphClockSelection = RCC_PERIPHCLK_I2C1;
PeriphClkInit.I2c1ClockSelection = RCC_I2C1CLKSOURCE_HSI;
if (HAL_RCCEx_PeriphCLKConfig(&PeriphClkInit) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief I2C1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_I2C1_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 1 */
hi2c1.Instance = I2C1;
hi2c1.Init.Timing = 0x2000090E;
hi2c1.Init.OwnAddress1 = 0;
hi2c1.Init.AddressingMode = I2C_ADDRESSINGMODE_7BIT;
hi2c1.Init.DualAddressMode = I2C_DUALADDRESS_DISABLE;
hi2c1.Init.OwnAddress2 = 0;
hi2c1.Init.OwnAddress2Masks = I2C_OA2_NOMASK;
hi2c1.Init.GeneralCallMode = I2C_GENERALCALL_DISABLE;
hi2c1.Init.NoStretchMode = I2C_NOSTRETCH_DISABLE;
if (HAL_I2C_Init(&hi2c1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Configure Analogue filter
*/
if (HAL_I2CEx_ConfigAnalogFilter(&hi2c1, I2C_ANALOGFILTER_ENABLE) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Configure Digital filter
*/
if (HAL_I2CEx_ConfigDigitalFilter(&hi2c1, 0) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN I2C1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END I2C1_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief TIM6 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_TIM6_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM6_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM6_Init 0 */
TIM_MasterConfigTypeDef sMasterConfig = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM6_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM6_Init 1 */
htim6.Instance = TIM6;
htim6.Init.Prescaler = 50-1;
htim6.Init.CounterMode = TIM_COUNTERMODE_UP;
htim6.Init.Period = 0xffff;
htim6.Init.AutoReloadPreload = TIM_AUTORELOAD_PRELOAD_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIM_Base_Init(&htim6) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sMasterConfig.MasterOutputTrigger = TIM_TRGO_RESET;
sMasterConfig.MasterSlaveMode = TIM_MASTERSLAVEMODE_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIMEx_MasterConfigSynchronization(&htim6, &sMasterConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM6_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END TIM6_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART2 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 1 */
huart2.Instance = USART2;
huart2.Init.BaudRate = 38400;
huart2.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart2.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart2.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart2.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart2.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart2.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
huart2.Init.OneBitSampling = UART_ONE_BIT_SAMPLE_DISABLE;
huart2.AdvancedInit.AdvFeatureInit = UART_ADVFEATURE_NO_INIT;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOF_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PA1 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_1;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
#ifdef USE_FULL_ASSERT
/**
* @brief Reports the name of the source file and the source line number
* where the assert_param error has occurred.
* @param file: pointer to the source file name
* @param line: assert_param error line source number
* @retval None
*/
void assert_failed(uint8_t *file, uint32_t line)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 6 */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the file name and line number,
tex: printf(“Wrong parameters value: file %s on line %d\r\n”, file, line) */
/* USER CODE END 6 */
}
#endif /* USE_FULL_ASSERT */
/************************ (C) COPYRIGHT STMicroelectronics *****END OF FILE****/
Hello,
I might have gotten a little closer to figuring out why the hard-coded DHT11 code may not be working for myself and some other students based on some observations.
I have hard-coded the following steps as required by the DHT11 from your guide:
PA6 is set as datapin (this is different)
1. Set pin PA6 as output pin, pull-up resistor enabled, and set pin ‘LOW’ for 18 milliseconds delay
2. Set pin PA6 as input pin, delay for 40 microseconds, check if pin PA6 is low
3. If PA6 is low, delay 80 microseconds, set response variable “Response = 1”
4. Wait for pin PA6 to go low in while loop
5. Collect 40 bits of data in for loop nested within for loop, if pin is high for 28 microseconds or less, bit is ‘0’, if pin is high for >28 microseconds, bit is ‘1’
6. Obtain temp and humidity from bit shift operations
The code shown below runs well and even shows 40 bits being transmitted by the DHT11 as shown by a digital usb analyzer:
//:0
The code for this is presented below. If I try to include anything from the while loop on to the end of the code to collect data, I get a complete flat-line as shown below. It won’t even run the initial code that I’ve proven to work.
//:0
In both cases where I leave steps 4 – 6 out and when I include them, I make sure to put 3 seconds delay before reading the sensor again so as to rule this out. Any reason why the code refuses to work entirely with just the addition of that while loop?
#include “stm32f4xx.h” // Device header
#include “stdio.h”
#include “stdint.h”
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void USART2_Init(void);
float TEMP, HUM;
void USART2_write(uint8_t* charString, uint16_t len);
void delayMicroseconds(uint32_t microseconds);
int main(void){
uint8_t DHT11_DATA[5] = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0};
uint8_t i, j = 0;
while(1){
RCC->AHB1ENR |= 0x1; //ENABLE GPIOA clock
GPIOA->MODER |= 0x1000; //Set pin PA6 as output mode
GPIOA->PUPDR |= 0x1000; //Pull-up resistor set for PA6
GPIOA->ODR &= ~0x40; //Set PA6 to LOW
delayMicroseconds(18000); //delay for 18 milliseconds
GPIOA->MODER &= ~0x1000; //Set pin PA6 as input mode*/
int Response = 0;
delayMicroseconds(40);
if(!(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40)) //
{
delayMicroseconds(80);
if(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40)
{
Response = 1;
}else{
Response = -1;
}
}
//while(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40); //Wait for pin to go low. DHT11 doesn’t run at all when this piece of code is active
/****This code left out until while loop shown to work*******************
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
for(j = 0; j < 8; j++)
{
while(!(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40)){}; //wait here while pin is low
delayMicroseconds(40);
if(!(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40))
{
DHT11_DATA[i] &= ~(1 << (7 – j)); //write 0 to bit
}
else DHT11_DATA[i] |= (1 << (7 – j)); //write 1 to bit
while(GPIOA->IDR & 0x40){}; //while pin is HIGH, hold here
}
}
TEMP = (float)DHT11_DATA[2];
HUM = (float)DHT11_DATA[0];
**************This code left out until while loop shown to work**********
delayMicroseconds(3000000);
}
}
static inline void delayMicroseconds(uint32_t microseconds)
{
RCC->APB1ENR |= 0x1; //ENABLE TIM2 clock
TIM2->PSC = 16 – 1;
TIM2->ARR = microseconds;
TIM2->CNT = 0;
TIM2->CR1 = 1;
while(!(TIM2->SR & 1)){};
TIM2->SR &= ~1;
TIM2->CR1 |= 0;
}
Hi
Thanks for your good job
My sensor worked with library but in this code it returns 255 or -1 as response
I know connection is ok
Can u help me?
check in the video description, i have posted one alternate code. That might help you
I ALSO HAVE PROBLEMS LIKE THIS. PLEASE HELP YOU HAVE RESOLVED
check the connection, pull up resistor etc
check timer frequency and make sure you are getting 1 us delay
try using that alternate code with DWT
Thank you for the tutorial. The code you created works very well. But there is a problem, the program can run properly in debug mode only. Without debugging i have to do a hard reset/power reset before the program can run. I use STM32F103C8 and Nucleo-L476RG.
thank you for helping out with this sensor …I have a project on gas sensor MQ2 ..Can u help me with the code for it with STM32 using CubeMx ….really need ur help?
I think i told u this already. It’s an ADC sensor, so just use the adc in that. If you have any problem, mail me admin@controllerstech.com
same the way, My code run only 1 time? :((
No Change humidity and temperature if I impact to it
what controller are u using ?
stm32f103c8t6
stm32f103c8t6
The code is alright. I tested it 2 days ago, and it was working fine. Maybe the connection, or the sensor… Try using the PULL UP Register, that might solve the issue
Hi, did you find the solution? I am facing the same problem
Hi! I’m using your code to get data from a DHT11 sensor on a STM32L053 by adapting it to work with 32Mhz clock and such… However the first acquisition goes ok and returns correct values on temp and humidity, but on the second loop it gets stuck on the check response function, it won’t leave the while loop waiting for the pin to go low. I’m using a 4.7K pull-up resistor on data pin… Any ideas? Thanks
try adding the delay of 500 ms or something between the acquisitions.
can u please check the code.I have put the timer also still it is not working .please help me …urgent
#include “main.h”
/* Private includes ———————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef ———————————————————–*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ————————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro ————————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ———————————————————*/
TIM_HandleTypeDef htim1;
UART_HandleTypeDef huart2;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes ———————————————–*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_TIM1_Init(void);
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ———————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
extern TIM_HandleTypeDef htim1;
void delay (uint32_t time)
{
/* change your code here for the delay in microseconds */
__HAL_TIM_SET_COUNTER(&htim1, 0);
while ((__HAL_TIM_GET_COUNTER(&htim1))<time);
}
#define DHT11_PORT GPIOA
#define DHT11_PIN GPIO_PIN_1
uint8_t Rh_byte1, Rh_byte2, Temp_byte1, Temp_byte2;
uint16_t sum, RH, TEMP;
uint8_t check = 0;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
void set_gpio_output (void)
{
/*Configure GPIO pin output: PA2 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_PIN;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void set_gpio_input (void)
{
/*Configure GPIO pin input: PA2 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_PIN;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void DHT11_start (void)
{
set_gpio_output (); // set the pin as output
HAL_GPIO_WritePin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN, 0); // pull the pin low
delay (18000); // wait for 18ms
set_gpio_input (); // set as input
}
void check_response (void)
{
delay (40);
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)))
{
delay (80);
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))) check = 1;
}
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
uint8_t read_data (void)
{
uint8_t i=0,j;
for (j=0;j<8;j++)
{
while (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go high
delay (40); // wait for 40 us
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)) == 0) // if the pin is low
{
i&= ~(1<<(7-j)); // write 0
}
else i|= (1<<(7-j)); // if the pin is high, write 1
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
return i;
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration——————————————————–*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_TIM1_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
DHT11_start ();
check_response ();
Rh_byte1 = read_data ();
Rh_byte2 = read_data ();
Temp_byte1 = read_data ();
Temp_byte2 = read_data ();
sum = read_data();
HAL_Delay(500);
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
/**
* @brief System Clock Configuration
* @retval None
*/
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
/** Configure the main internal regulator output voltage
*/
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_PWR_VOLTAGESCALING_CONFIG(PWR_REGULATOR_VOLTAGE_SCALE2);
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB busses clocks
*/
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLM = 4;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLN = 84;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLP = RCC_PLLP_DIV2;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLQ = 7;
if (HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/** Initializes the CPU, AHB and APB busses clocks
*/
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK
|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1|RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
if (HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
/**
* @brief TIM1 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_TIM1_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM1_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END TIM1_Init 0 */
TIM_ClockConfigTypeDef sClockSourceConfig = {0};
TIM_MasterConfigTypeDef sMasterConfig = {0};
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM1_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END TIM1_Init 1 */
htim1.Instance = TIM1;
htim1.Init.Prescaler = 84-1;
htim1.Init.CounterMode = TIM_COUNTERMODE_UP;
htim1.Init.Period = 0xffff-1;
htim1.Init.ClockDivision = TIM_CLOCKDIVISION_DIV1;
htim1.Init.RepetitionCounter = 0;
htim1.Init.AutoReloadPreload = TIM_AUTORELOAD_PRELOAD_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIM_Base_Init(&htim1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sClockSourceConfig.ClockSource = TIM_CLOCKSOURCE_INTERNAL;
if (HAL_TIM_ConfigClockSource(&htim1, &sClockSourceConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
sMasterConfig.MasterOutputTrigger = TIM_TRGO_RESET;
sMasterConfig.MasterSlaveMode = TIM_MASTERSLAVEMODE_DISABLE;
if (HAL_TIMEx_MasterConfigSynchronization(&htim1, &sMasterConfig) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN TIM1_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END TIM1_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief USART2 Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 0 */
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 1 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 1 */
huart2.Instance = USART2;
huart2.Init.BaudRate = 115200;
huart2.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart2.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart2.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart2.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart2.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart2.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart2) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN USART2_Init 2 */
/* USER CODE END USART2_Init 2 */
}
/**
* @brief GPIO Initialization Function
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
/* GPIO Ports Clock Enable */
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOH_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
/*Configure GPIO pin Output Level */
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LD2_GPIO_Port, LD2_Pin, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
/*Configure GPIO pin : B1_Pin */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = B1_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_IT_FALLING;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(B1_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pin : PA1 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = GPIO_PIN_1;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStruct);
/*Configure GPIO pin : LD2_Pin */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = LD2_Pin;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(LD2_GPIO_Port, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */
/* USER CODE END 4 */
/**
* @brief This function is executed in case of error occurrence.
* @retval None
*/
void Error_Handler(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN Error_Handler_Debug */
/* User can add his own implementation to report the HAL error return state */
/* USER CODE END Error_Handler_Debug */
}
you did not start the timer. Put hal_tim_base_start inside the main function
Could u please tell me where in the main function ?
And which pin shall I use as the data pin for the sensor if using stm32f401re and should it be gpio input or gpio output?
put in between these 2
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
you can use any pin. If it’s not working, try adding a pull up register to the data pin
thank you so much
can u please check my code i have tried multiple times but it is still coming as zero please help me .i have to submit my project
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body
******************************************************************************
* @attention
*
* © Copyright (c) 2020 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This software component is licensed by ST under BSD 3-Clause license,
* the “License”; You may not use this file except in compliance with the
* License. You may obtain a copy of the License at:
* opensource.org/licenses/BSD-3-Clause
*
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
/* Includes ——————————————————————*/
#include “main.h”
#include “stdio.h”
/* Private includes ———————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */
#include “dwt_stm32_delay.h”
/* USER CODE END Includes */
/* Private typedef ———————————————————–*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PTD */
/* USER CODE END PTD */
/* Private define ————————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PD */
/* USER CODE END PD */
/* Private macro ————————————————————-*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PM */
#define DHT11_PORT GPIOA
#define DHT11_PIN GPIO_PIN_9
/* USER CODE END PM */
/* Private variables ———————————————————*/
UART_HandleTypeDef huart2;
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
uint8_t Rh_byte1, Rh_byte2, Temp_byte1, Temp_byte2;
uint16_t sum;
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct;
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private function prototypes ———————————————–*/
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART2_UART_Init(void);
/* USER CODE BEGIN PFP */
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* With GCC, small printf (option LD Linker->Libraries->Small printf
set to ‘Yes’) calls __io_putchar() */
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int __io_putchar(int ch)
#else
#define PUTCHAR_PROTOTYPE int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
/* USER CODE END PFP */
/* Private user code ———————————————————*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
void set_gpio_output (void)
{
/*Configure GPIO pin output: PA7 – to this DHT11 output is connected */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_PIN; //Pin5 is selected
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP; //Mode is output push-pull
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW; //GPIO clock frequency selected as low
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct); //Initialize Pin5 of GPIO Port A
}
//To Configure PA7 as input
void set_gpio_input (void)
{
/*Configure GPIO pin input: PA2 */
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = DHT11_PIN;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_INPUT;
GPIO_InitStruct.Pull = GPIO_NOPULL;
HAL_GPIO_Init(DHT11_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void DHT11_start (void)
{
set_gpio_output (); // set the pin as output
HAL_GPIO_WritePin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN, 0); // pull the pin low
DWT_Delay_us (18000); // wait for 18ms
set_gpio_input (); // set as input for receiving data
}
void check_response (void)
{
DWT_Delay_us (40); //wait for 40us
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))==0) // read PA5 pin & check if the pin PA5 is low
{
DWT_Delay_us (80); //wait for 80us
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))==1)
{
//printf(“Check response ok”); //Check if the pin is high. If it is, than the response is ok.
}
}
//This will totally be a delay of 120us and the pin should be high now.
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))==1); // wait for the pin to go low
}
uint8_t read_data (void)
{
uint8_t i=1,j;
for (j=0;j<8;j++)
{
while (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go high
/* wait for 40 us. This is because the length of “0” bit is 26-28us
* and if the pin is high after 40us, it indicates that the bit is “1”.
* */
DWT_Delay_us (40); //This function is included from library dwt_stm32_delay.h to give delay in microseconds
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN)) == 0) // if the pin is low
{
i&= ~(1<<(7-j)); // write 0
}
else i|= (1<<(7-j)); // if the pin is high, write 1
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (DHT11_PORT, DHT11_PIN))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
return i;
}
/* USER CODE END 0 */
/**
* @brief The application entry point.
* @retval int
*/
int main(void)
{
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
/* USER CODE END 1 */
/* MCU Configuration——————————————————–*/
/* Reset of all peripherals, Initializes the Flash interface and the Systick. */
HAL_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN Init */
/* USER CODE END Init */
/* Configure the system clock */
SystemClock_Config();
/* USER CODE BEGIN SysInit */
/* USER CODE END SysInit */
/* Initialize all configured peripherals */
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART2_UART_Init();
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
/* USER CODE END 2 */
/* Infinite loop */
/* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */
while (1)
{
/* USER CODE END WHILE */
printf("\n\r Entering in the while loop of code\n\r");
DHT11_start (); //Initialize DHT11
check_response (); //Check response from DHT11
Rh_byte1 = read_data (); //Read date i.e. Relative Humidity – first byte
Rh_byte2 = read_data (); //Read date i.e. Relative Humidity – second byte
Temp_byte1 = read_data (); //Read date i.e. Temperature – first byte
Temp_byte2 = read_data (); //Read date i.e. Temperature – second byte
sum = read_data(); //Read checksum data
if (sum == (Rh_byte1+Rh_byte2+Temp_byte1+Temp_byte2)) // if the data is correct
{
printf("\n\rRelative Humidity value is: %c%c percentage",((Rh_byte1/10)+48),((Rh_byte1%10)+48));
printf("\n\rTemperature value is: %c%c Celcius",((Temp_byte1/10)+48),((Temp_byte1%10)+48));
}
else
{
printf("\n\r Checksum not matched..Incorrect data from DHT11\n\r");
}
HAL_Delay(1000);
/* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */
}
/* USER CODE END 3 */
}
use timer delay instead of DWT
can u please tell me where to put the timer delay function in the code ?
can u modify in this code and tell me please i have to submit my code in two days
The code is already modified to use the timer for the delay. You can download it.
Can you tell me the code for MQ6 GAS Sensor
The code shown in the video is not the same in downloads. Can the code be updated to enable people to learn?
The code is pretty much the same. Only the delay part has been changed. DWT doesn’t work properly as many of the users complained about it, so i have modified the delay to use the timer.
Please read the post carefully. I have linked the video which explains how to use timer to create the delay.
i did this programm with delays for DHT22 and i got 0 warnings and 0 errors, but from sensor i see 0, and LCD just lights (any on it). Can I send project to you? Im very pleased
Best regards Man
This tutorial is for dht11, so how will it work for DHT22?
Search for DHT22 in the website, there is another tutorial available for that.
yes it is. but it dont even work too. on official ST Cube MX ofcourse. it is dont debug or compile
in function: uint8_t read_data should not be: DWT_Delay_us(50) rather than: DWT_Delay_us(40) ?
In Datasheet is written: “When DHT is sending data to MCU, every bit of data begins with the 50us low-voltage-level”
I understand your confusion. Actually 40us is not the starting sequence.
We will wait for the pin to go high ( this wait is 50 us, the start sequence)
Now once the pin is high, the sensor can either send a low (27 us high) or a high (70 us high) so to be on the safe side, we will check the pin after 40us. If its low, that means signal was low and if high, means signal is high.
Ok, so I understand that we will check the pin after 40us (not 50us) just to be on the safe side.
Hi ControllersTech Team,
I appreciate for your work related to DHT11 with STM32 however I am getting stuck in the [ check response ] function & not sure what is the exact problem here. With the debugging what I observed is that it stucks in while loop within the check_response function…
It will be highly appreciated to have your guidance.
This might have something to do with the pull-up resistor. Check that the resistor is connected properly
Could you help me with this function? The check variable always returns check = 0.
And when I run debug the Debugger pop-up is: Cannot access target. Shutting down debug session.
void DHT11_start (void)
{
set_gpio_output (); // set the pin as output
HAL_GPIO_WritePin (GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, 0); // pull the pin low
DWT_Delay_us (18000); // wait for 18ms
set_gpio_input (); // set as input
}
void check_response (void)
{
DWT_Delay_us (40);
if (!(HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0)))
{
DWT_Delay_us (80);
if ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0))) check = 1;
printf(“DHT11_Response = %d”, check);
}
printf(“DHT11_Response = %d”, check);
while ((HAL_GPIO_ReadPin (GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0))); // wait for the pin to go low
}
Have u done the debugging before ?
It might be problem with the connection with the computer
Share ur code at help@157.245.140.16
Full code including the cubemx file
Can you help me how connecting stm32f103c8t6 with Dht11. Thank!
Can you help me how connect dht11 with stm32f103c.Thank!
Hi, where is the ” dwt_stm32_delay.h and .c ” , also ” i2c-lcd.h and .h “. I need it asap please. Many thanks.
Hey, Your website is just amazing, I really admire it. I was just wondering – woudn’t be easier to set GPIO pin in open-drain mode instead writing set_gpio_output and set_gpio_input functions?
Greetings,
Marek
this is my code if you don’t mind check it with me to be useful
There is a tutorial about DHT22 also. Plz use search in the website
uint8_t Rh_byte1, Rh_byte2, Temp_byte1, Temp_byte2;
uint16_t sum, RH, TEMP;
uint8_t check = 0;
void DHT22_Out(void){
RCC_AHB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHB1Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure ;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_1;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_OUT;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_OType = GPIO_OType_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_25MHz ;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_PuPd = GPIO_PuPd_NOPULL;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
}
void DHT22_In(void){
RCC_AHB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_AHB1Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure ;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_1;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_OType = GPIO_OType_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_25MHz ;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_PuPd = GPIO_PuPd_NOPULL;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
}
void DHT22_Start(void){
DHT22_Out();
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_1,Bit_RESET);
Delay(500);
GPIO_WriteBit(GPIOA, GPIO_Pin_1, Bit_SET);
Delay(30);
DHT22_In();
}
void Check_Response(void){
Delay(40);
if(!GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1))
{
Delay(80);
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1)) check=1;
}
while(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1));
}
uint8_t Read_Data(void){
uint8_t i, j ;
for (j=0; j<8 ; j++){
while(!GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1));
Delay(40);
if(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1)==0){
i&= ~(1<<(7-j));
}else{
i|= (1<<(7-j));
}
while(GPIO_ReadInputDataBit(GPIOA,GPIO_Pin_1));
}return(i);
}
int main(void)
{
while(1){
DHT22_Start();
Check_Response();
Rh_byte1=Read_Data();
Rh_byte2=Read_Data();
Temp_byte1=Read_Data();
Temp_byte2=Read_Data();
sum=Read_Data();
//if (sum == (Rh_byte1+Rh_byte2+Temp_byte1+Temp_byte2))
{
TEMP = ((Temp_byte1<<8)|Temp_byte2);
RH = ((Rh_byte1<<8)|Rh_byte2);
}
Delay(1000);
}
what is Delay function ??
can u share the code..
Hi , could you send to me the ” i2c-lcd.c and .h ” also ” dwt_stm32_delay.c and .h ” , I did’t find them, Please I need it asap. Many thanks.
thank you for this tutoriel, it’s a perfect job ^^
i try to modify your code to read values from DHT22, i modify the time like it was in the datasheet but i don’t understand why the sensor returns 0, i use an stm32f4Discovery without LCD could you help me plz !!
good