Last Updated: September 25, 2025
STM32 USB CDC Example – Virtual COM Port Communication (No UART Needed)
This tutorial explains how to set up a STM32 USB CDC (Virtual COM Port) for bidirectional communication with a PC—no UART required. You’ll learn how to use the STM32CubeMX tool to configure USB as a Communication Device Class (CDC) and implement both CDC_Transmit_FS and CDC_Receive_FS to send and receive data directly via USB. This is a perfect method for STM32 USB virtual COM port applications like logging, file transfer, and serial communication over USB—especially useful when UART pins are limited or unavailable.
Up to this point, we have relied on UART communication to interface with the computer, enabling the transmission and reception of useful data. Many STM32 development boards, such as the Nucleo and Discovery series, include an on-board ST-Link debugger, which also provides a Virtual COM Port. This feature simplifies the process of sending data to the computer over UART without the need for additional external hardware.
However, when working with custom boards—such as the popular Bluepill board—there is no built-in ST-Link. In such cases, an external USB-to-UART converter module is typically required to enable data transfer between the microcontroller and the computer.
In this tutorial, we will explore how to utilize the USB peripheral of STM32 to communicate directly with a PC, eliminating the need for UART. You will learn how to configure STM32 USB to both send and receive data, in a manner similar to traditional UART communication.
STM32 USB PC Communication Video Tutorial
This tutorial explains how to set up USB CDC on STM32 to communicate directly with your PC, without using UART. To make it easier to follow, I’ve recorded a step-by-step video walkthrough showing the CubeMX configuration, code changes, and a live demo of sending and receiving data. Watch the video while working with the example code to clearly understand each step of the process.
Watch the USB CDC TutorialIntroduction to STM32 USB Communication
When working with STM32 microcontrollers, we often use UART to send and receive data between the board and a PC. However, STM32 also has a powerful feature called USB Communication Device Class (USB CDC). With USB CDC, your STM32 can communicate directly with a computer over USB, just like a virtual COM port, without needing a USB-to-UART converter. This makes STM32 USB communication faster, more reliable, and easier to set up for many IoT and embedded projects.
Why use USB instead of UART for PC communication
Traditionally, developers use UART with a USB-to-serial adapter to connect STM32 to a PC. While this works, it adds extra hardware and limits speed. By using STM32 USB CDC, you connect the board directly to your PC’s USB port. This approach removes the need for converters, reduces wiring, and offers higher data transfer rates. It also allows you to run multiple virtual COM ports if your project requires more than one channel of communication. In short, USB provides cleaner, faster, and more efficient communication than UART when working with STM32.
What is USB CDC (Communication Device Class)
USB CDC, or Communication Device Class, is a standard USB protocol that lets devices act as virtual serial ports. When you enable USB CDC on STM32, your computer recognizes the board as a Virtual COM Port (VCP). This means you can use the same serial terminal software you use for UART—like PuTTY, Tera Term, or Arduino Serial Monitor—to exchange data over USB. For developers, this makes the transition from UART to USB seamless, while unlocking the benefits of direct USB communication.
Features of USB CDC in STM32:
- Virtual COM Port Emulation:
Creates a virtual serial port on the PC, enabling standard serial communication without physical UART hardware. - High-Speed Data Transfer:
Supports faster data rates compared to traditional UART, limited only by USB specifications. - Plug-and-Play Support:
Works seamlessly with most operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS) without requiring specialized drivers. - Bidirectional Data Exchange:
Enables simultaneous data transmission and reception, making it suitable for real-time communication applications.
STM32 USB CDC Project Requirements
Before we begin building our STM32 ESP8266 MQTT project, let’s take a quick look at the tools and components you’ll need. This includes both hardware and software required for the project.
- Hardware:
- STM32F103 Dev Board
- ST-Link V2
- USB Cable
- Software:
- STM32CubeIDE
- Serial Monitor
STM32 USB CDC CubeMX Configuration
Before you can start sending and receiving data with STM32 over USB, you need to configure the USB peripheral in STM32CubeMX.
Enabling USB peripheral in STM32CubeMX
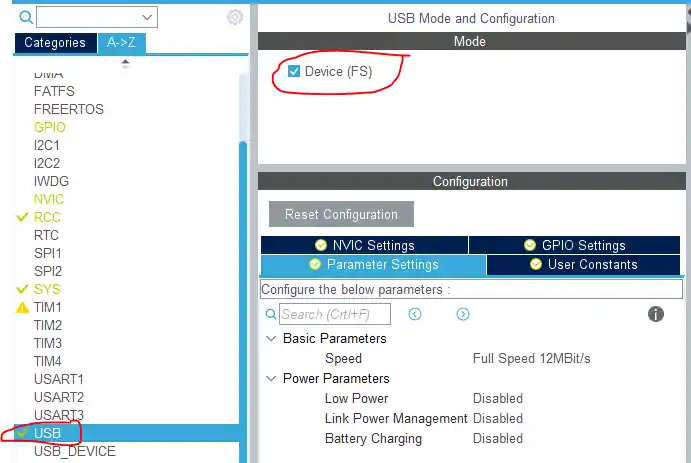
First, open STM32CubeMX and select your target STM32 microcontroller. In the Peripherals tab, locate and enable the USB Device (FS) or USB OTG FS peripheral, depending on your board. Make sure to choose Device Only mode, since we are using STM32 as a USB device connected to a PC.
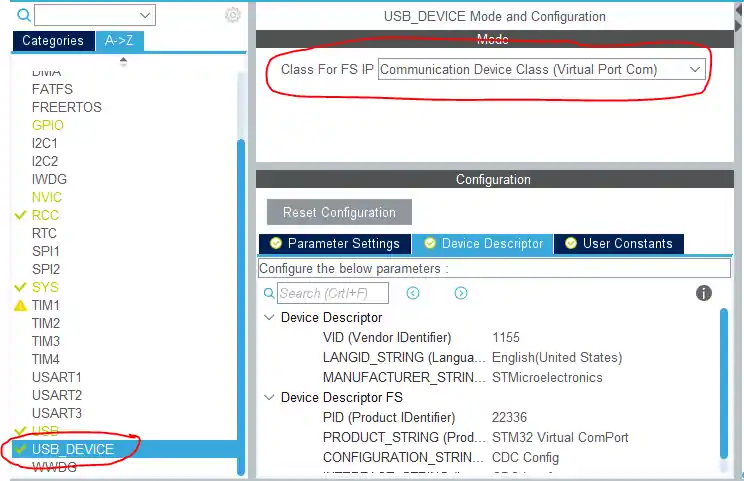
Configuring USB as a Virtual COM Port
Next, configure the USB device to work as a Communication Device Class (CDC). In CubeMX, go to the USB configuration settings and select CDC (Communication Device Class). This tells STM32 to act like a Virtual COM Port (VCP), making it appear as a serial port on your PC. You can also adjust endpoint sizes and buffer settings here to optimize data transfer for your application.
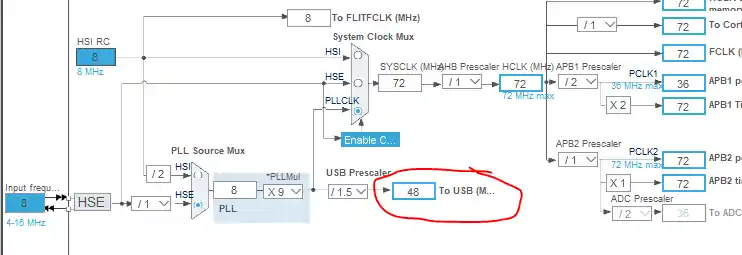
Setting the STM32 USB Clock
A correct USB clock configuration is essential for reliable STM32 USB communication. The USB peripheral requires a precise 48 MHz clock to function properly. Without this, your USB CDC virtual COM port may not work, and data transmission can fail.
STM32 USB CDC Code Implementation
To send data to a PC using USB CDC, we need to use specific functions provided in the STM32 USB middleware. These functions are implemented in the following file:
USB_DEVICE -> App -> usbd_cdc_if.cUsing CDC_Transmit_FS to Send Data to PC
Once your STM32 USB CDC is set up, you can start sending data from the microcontroller to your PC using the CDC_Transmit_FS function. This function is part of the STM32 HAL USB CDC library and makes sending messages over USB straightforward.
How CDC_Transmit_FS Works
The CDC_Transmit_FS function sends a buffer of data from your STM32 to the PC through the virtual COM port. Its basic syntax looks like this:
uint8_t CDC_Transmit_FS(uint8_t* Buf, uint16_t Len);Buf– Pointer to the data buffer you want to send.Len– Number of bytes to transmit.
When called, CDC_Transmit_FS queues the data for transmission over USB. Your PC will receive this data just like it would from a normal serial port.
Example Code for Data Transmission
#include "main.h"
#include "usb_device.h"
#include "usbd_cdc_if.h"
#include "string.h"
/* Private user code ---------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN 0 */
uint8_t *data = "Hello World from USB CDC\n";
/* USER CODE END 0 */
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USB_DEVICE_Init(); // Initialize the USB device stack
while (1)
{
CDC_Transmit_FS(data, strlen(data)); // Send data via USB
HAL_Delay(1000); // Wait for 1 second
}
}Step-by-Step Explanation of the Code
- Include Headers:
The required header files (usb_device.h,usbd_cdc_if.h, andstring.h) are included to use USB functions and string operations. - Define Data Buffer:
We define a pointerdatacontaining the string"Hello World from USB CDC\n", which will be transmitted. - Initialization:
HAL_Init()– Initializes the HAL Library.SystemClock_Config()– Configures the system clock.MX_GPIO_Init()– Initializes the GPIOs.MX_USB_DEVICE_Init()– Sets up the USB device for CDC communication.
- Data Transmission Loop:
Inside thewhile(1)loop, the functionCDC_Transmit_FS()sends the content ofdataevery 1 second usingHAL_Delay(1000).
Verifying Data on the PC
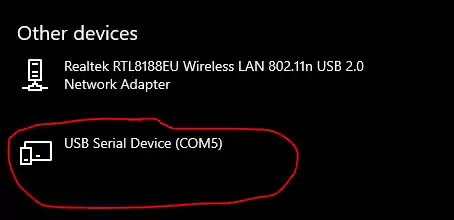
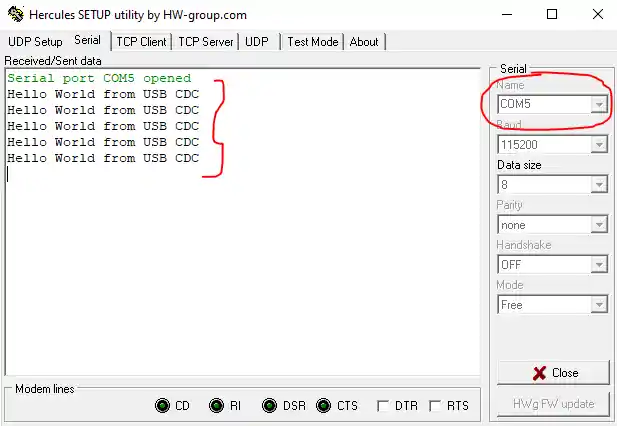
After you run your STM32 code, the PC automatically detects the board as a Virtual COM Port (VCP). This confirms that the USB CDC setup is working correctly. You can now view the data sent from your STM32 using any serial terminal software.
- When the code runs on the MCU, the PC detects the STM32 as a Virtual COM Port (VCP).
- Open any serial monitor software (e.g., Hercules, Tera Term, or PuTTY) and select the correct COM port.
- You will see the message “Hello World from USB CDC” printed every second.
Using CDC_Receive_FS to receive Data from PC
After sending data from STM32 to your PC, you often need to receive data back from the PC. The STM32 HAL library provides the CDC_Receive_FS function to handle incoming data over USB CDC. This function lets your board act like a true serial device, reading messages sent from the computer in real time.
How CDC_Receive_FS Works
The CDC_Receive_FS function is a callback that automatically executes when the PC sends data. CubeMX-generated code links this function to the USB CDC driver, so you don’t need to manage low-level USB packets manually.
Basic usage example:
uint8_t USB_RxBuffer[64]; // Buffer to store received data
uint8_t CDC_Receive_FS(uint8_t* Buf, uint32_t *Len) {
memcpy(USB_RxBuffer, Buf, *Len); // Copy received data to buffer
// Process the received data here
return USBD_OK;
}Buf– Points to the data received from the PC.Len– Number of bytes received.- Return
USBD_OKto signal successful reception.
Example: Echoing Data Back to PC
You can combine CDC_Receive_FS with CDC_Transmit_FS to echo messages back to the PC, which is useful for testing:
uint8_t CDC_Receive_FS(uint8_t* Buf, uint32_t *Len) {
// Copy received data to buffer
memcpy(USB_RxBuffer, Buf, *Len);
// Send it back to PC
CDC_Transmit_FS(Buf, *Len);
return USBD_OK;
}This setup allows STM32 to receive any message typed on the PC and immediately send it back, confirming two-way USB communication.
Tips for Using CDC_Receive_FS
- Use a sufficient buffer – Ensure the buffer can hold the largest expected message from the PC.
- Process data quickly – Avoid long delays inside the callback to prevent USB communication issues.
- Combine with interrupts – For continuous communication, process received data in the main loop or in a separate task after copying it from the callback.
Using CDC_Receive_FS makes your STM32 USB CDC communication fully bidirectional, eliminating the need for UART while enabling real-time interaction with your PC.
Advantages of STM32 USB CDC over UART
Using STM32 USB CDC instead of traditional UART offers several important benefits. It makes your PC communication faster, cleaner, and more flexible.
Faster Data Transfer Speed
USB CDC provides higher data transfer rates compared to UART. With USB, STM32 can send and receive larger amounts of data quickly, making it ideal for applications that require frequent or high-volume communication. This speed improvement helps reduce latency and ensures smoother data logging and control tasks.
Direct PC Connectivity (No USB-UART Converter Needed)
Unlike UART, USB CDC allows the STM32 to connect directly to a PC. You don’t need a USB-to-UART converter or extra wiring. The STM32 appears as a Virtual COM Port on the PC, so you can use standard serial terminal software like PuTTY, Tera Term, or Hercules. This simplifies setup and reduces hardware costs.
Reliable Bidirectional Communication
USB CDC supports full bidirectional communication, meaning you can send data from STM32 to the PC and receive data back at the same time. Unlike UART, which may require additional circuitry for multiple channels, USB CDC provides a stable and reliable two-way communication channel out of the box.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting STM32 USB CDC
Even with a correct setup, you may face some common issues when using USB CDC on STM32. Here’s how to identify and fix them.
Virtual COM Port Not Showing Up on PC
If your PC does not detect the STM32 as a Virtual COM Port:
- Check that the USB cable is working and supports data transfer (some cables are power-only).
- Ensure the USB peripheral is enabled in CubeMX.
- Verify that the USB drivers are installed on your PC.
Data Not Transmitting or Receiving Correctly
If data does not appear on the PC or seems corrupted:
- Confirm that you are using the correct COM port and settings in your terminal software.
- Make sure the STM32 code calls
CDC_Transmit_FSandCDC_Receive_FScorrectly. - Avoid sending data too quickly without checking for previous transmission completion.
Driver and Firmware Related Issues
Some problems arise due to outdated or missing drivers:
- Update your USB VCP drivers for Windows, macOS, or Linux.
- Ensure CubeMX generates the latest USB CDC firmware for your STM32.
- If using custom USB code, verify that endpoint sizes, buffer lengths, and descriptors are configured correctly.
STM32 USB CDC Result
The result of the above code is shown in the images below
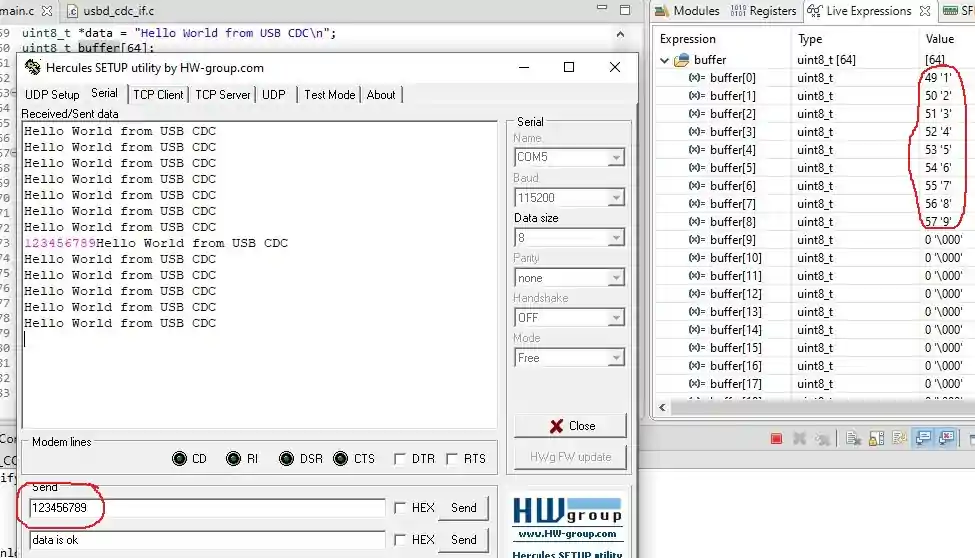
The controller was keep transmitting “Hello World from USB CDC“. When the PC sent the data “123456789” (Represented by Pink colour on the console) to the controller, it gets stored in the buffer.
You can see the data stored in the buffer in the debugger’s Live Expression window as shown in the image above.
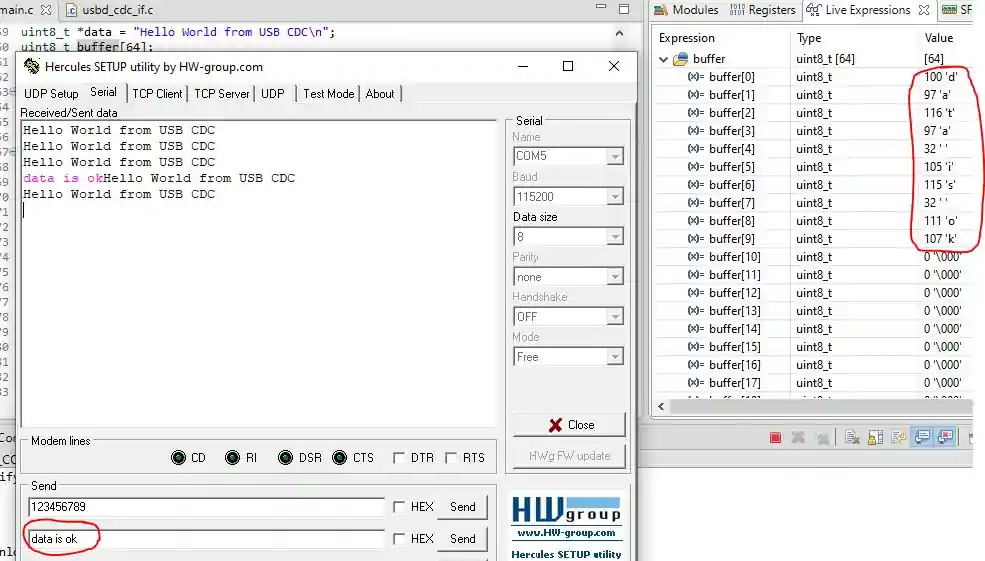
The same behavior was observed in this case as well. This time, a different set of data was transmitted, and it was successfully stored in the buffer.
Since the buffer is accessible from the main.c file, the received data can be processed further in any desired manner, such as parsing commands, logging information, or triggering specific application tasks.
Conclusion
Using STM32 USB CDC allows you to communicate with a PC without using UART, making your projects faster, cleaner, and more reliable. By setting up the USB peripheral in STM32CubeMX, configuring it as a Virtual COM Port, and using CDC_Transmit_FS and CDC_Receive_FS, you can send and receive data seamlessly.
USB CDC offers higher data transfer speeds, direct PC connectivity, and stable bidirectional communication, making it a superior choice over traditional UART connections.
Even if you encounter issues like the Virtual COM Port not showing or data transmission problems, careful configuration and troubleshooting ensure smooth USB communication.
Browse More STM32 USB Tutorials
STM32 USB HOST MSC
STM32 USB HOST HID
Emulate STM32F103 as a MOUSE
How to use STM32 as a KEYBOARD
STM32 USB CDC Tutorial: Device and Host Example Using HAL + CubeMX
WavePlayer using STM32 Discovery
STM32 USB CDC Project Download
Info
You can help with the development by DONATING Below.
To download the project, click the DOWNLOAD button.
STM32 USB CDC FAQs
USB CDC (Communication Device Class) allows an STM32 microcontroller to emulate a Virtual COM Port over USB. This enables seamless data exchange with a PC, similar to UART, but without the need for an external USB-to-UART converter.
Most STM32 boards with a built-in USB peripheral support USB CDC. Boards like the Bluepill require enabling USB Device Mode in CubeMX and proper clock configuration to work as a Virtual COM Port.
You can use the CDC_Transmit_FS() function from the usbd_cdc_if.c file. It transmits data buffers directly to the PC over USB.
Data reception is handled inside the CDC_Receive_FS() callback. By defining a buffer in main.c and modifying this callback, you can store and process incoming data.
USB CDC provides faster data rates, does not require external hardware, and is recognized as a standard COM port by most operating systems, making development simpler and more efficient.







Hello Sir, hope you are doing well, i followed the steps from tutorial but the device is not showing up in com port of PC, i have tried different codes like led blink and all which works fine but the CDC doesn’t work , the code gets uploaded successfully , but no com port show on device manager . pls help.
Log output file: C:\Users\NW\AppData\Local\Temp\STM32CubeProgrammer_a05264.log
ST-LINK SN : 211405003212364D434B4E00
ST-LINK FW : V2J45S7
Board : —
Voltage : 3.19V
SWD freq : 4000 KHz
Connect mode: Under Reset
Reset mode : Hardware reset
Device ID : 0x410
Revision ID : Rev X
Device name : STM32F101/F102/F103 Medium-density
Flash size : 64 KBytes
Device type : MCU
Device CPU : Cortex-M3
BL Version : —
Opening and parsing file: ST-LINK_GDB_server_a05264.srec
Memory Programming …
File : ST-LINK_GDB_server_a05264.srec
Size : 29.15 KB
Address : 0x08000000
Erasing memory corresponding to segment 0:
Erasing internal memory sectors [0 29]
Download in Progress:
File download complete
Time elapsed during download operation: 00:00:01.887
Verifying …
Download verified successfully
Shutting down…
Exit.
Hi,
Thanks for the tenurial you have made.
please make and share another one for USB BULK TRANSFER application if it is viable for you.
many thanks
Thank you so much 🙏
I’m using a blue pill with stm32f103c8t6 using STlink-V2 when I flash the file to the blue pill the stlink disconnected and not able to debug and see the data I sent to the board.
How did you connect your blue pill board and stlink.
Very good tutorial.
Hi, how should I receive unknown length of data from usb com port?I know that such operation in uart could be done using Idle line detector. but how about usb cdc receive?
The function int8_t CDC_Receive_FS(uint8_t* Buf, uint32_t *Len) already receives the data of unknown length. Here Len is the pointer to the number of data byte received.
after I press the reset button, data is no longer received by Hercules. I had to reconnect the USB to get it working again. Is there a way to prevent that?
i am using STM32F413zh nucleo when i connect the micro-USB cable to PC there is nothing as appearance in device manager????
i connect D+ and D- in p12 and p11.
in device manage only st-link cable was showing.
what i do please help….
1. Why are you even doing this on the nucleo board ? You can simply send the data to the PC via the STlink using the UART2.
2. Nucleo STM32F413zh has one user USB at the bottom. Use it.
Salut, j’utilise un STM32H735G-DK. J’ai suivi votre tuto, et vu que les désignations de fonction diffèrent (STM32F & STM32H) j’ai du modifier le “F” de CDC_Transmit_FS par “H” ce qui m’a donné CDC_Transmit_HS. Malgré toutes mes tentatives, mon pc ne détecte pas le port vituel de mon MCU. Svp j’ai besoin d’aide . . . vous pouvez me contacter à mon adresse m.a.i.l: karimnana520 @gmail.com ou sur mon whatsapp actuel: +237 658747103
USB HS Does not supports virtual Communication. You have to use FS only
I’m using stm32f429zit6 but my board is not detected by hercule. what am i do?
if you are using the nucleo or discovery boards, make sure you connect to the USER USB, not the ST-Link
Also check if the cable supports the data transfer or not
This tutorial in Stdlibrary instead please
How recieve packet from PC
B0=254; // sync
B1 //number of variable
B2//Low byte
B3// byte
B4// byte
B5=//High Byte
Var[B1]=B2+B3<<8+B4<<16+B5<<32
If the stream fails, then in the incoming stream we look for synchrobyte 254 (skip bytes until we have received 254)
how can i transmit a HEX value instead of char?
Thanks!
just send it simply. What’s the issue?
Hai, how can we send/transmit the adc value through the usb cdc virtual comfort, I am new to stm32 ,if anyone known please help me
try sending the address to the value.
If can’t, then convert it to string and send
https://www.digikey.com/en/maker/projects/getting-started-with-stm32-working-with-adc-and-dma/f5009db3a3ed4370acaf545a3370c30c
stm32f4 ws2812b with cubeide.
That great! You can make video with NRF24L01, please!
it’s great 😍
The USB_CDC_ReceivePacket is the acknowledge of receiving. It should be called after copy the data.