Last Updated: September 14, 2025
Modbus #6. STM32 as Slave || Write Registers
This is the 6th Tutorial in the Modbus Series, and we will continue to use the STM32 as a slave Device. This tutorial will cover how the STM32 as a slave device will send a response to the queries regarding writing a single and multiple Registers.
We will cover the function codes FC06 and FC16 in this tutorial, but from the slave prospective.
I have already covered the connection parameters in the previous tutorial, and we will continue with the same connection. in fact this is going to be the same project with a few additions in the modbusslave.c file.
I have just added the functions for writing single Register and multiple Registers in the modbusslave.c file. The rest of the project is pretty much the same as the previous one.
VIDEO TUTORIAL
You can check the video to see the complete explanation and working of this project.
Check out the Video Below
The Master Sotware
I am using the simply modbus master software, which can be downloaded from https://www.simplymodbus.ca/download.htm
So far we have used the master software for reading the Registers and coils from the slave device. Now we will use it for writing them.
In order to write the data into the slave device, we have to first open the “write” window in the software as shown below
Here inside the RED box if we click the write button, a new window will open. This is shown below
You might be already familiar with all the options shown in this window. We will see the use of the software later in the results section of this tutorial.
Some insight into the CODE
This is the same project in continuation, so I will only explain the parts that have been added in this particular tutorial.
Writing single Register
uint8_t writeSingleReg (void)
{
uint16_t startAddr = ((RxData[2]<<8)|RxData[3]); // start Register Address
if (startAddr>49) // The Register Address can not be more than 49 as we only have record of 50 Registers in total
{
modbusException(ILLEGAL_DATA_ADDRESS); // send an exception
return 0;
}
Holding_Registers_Database[startAddr] = (RxData[4]<<8)|RxData[5];
// Prepare Response
TxData[0] = SLAVE_ID; // slave ID
TxData[1] = RxData[1]; // function code
TxData[2] = RxData[2]; // Start Addr HIGH Byte
TxData[3] = RxData[3]; // Start Addr LOW Byte
TxData[4] = RxData[4]; // Reg Data HIGH Byte
TxData[5] = RxData[5]; // Reg Data LOW Byte
sendData(TxData, 6); // send data... CRC will be calculated in the function itself
return 1; // success
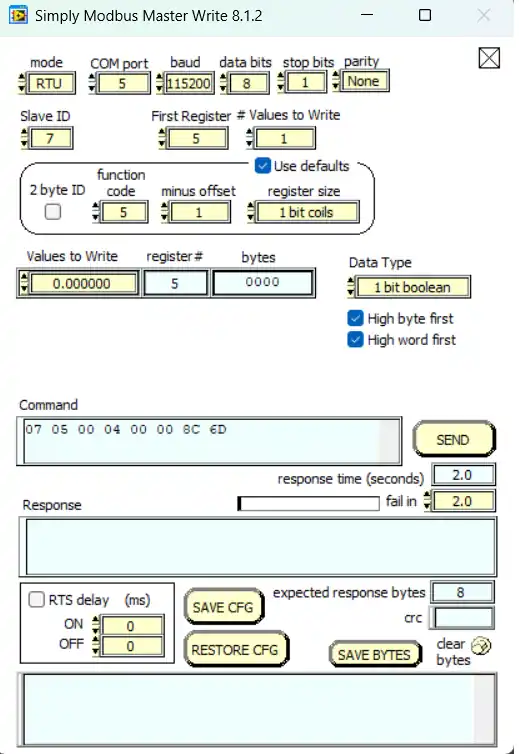
}In order to write a single register, the master simply send the Register address followed by the Data to write
- Here we first extract the Register address by using the RxData[2] and [3].
- If the address is more than 49, the slave will send an exception.
- This is because I have defined the database for only 50 Registers (0-49).
- Next we will combine the 2 bytes in RxData[4] and [5] into a single 16 bit value, and update the database with this value.
- The response sent by the slave in this case is exactly same as the query sent by the master.
- So we will copy the individual bytes from RxData into the TxData and send the Response.
Below you can see the query sent by the master software.
Below is the image showing the Respective register before and after the query was sent. You can see the value has been updated as per the data sent by the master.
Writing Multiple Registers
uint8_t writeHoldingRegs (void)
{
uint16_t startAddr = ((RxData[2]<<8)|RxData[3]); // start Register Address
uint16_t numRegs = ((RxData[4]<<8)|RxData[5]); // number to registers master has requested
if ((numRegs<1)||(numRegs>123)) // maximum no. of Registers as per the PDF
{
modbusException (ILLEGAL_DATA_VALUE); // send an exception
return 0;
}
uint16_t endAddr = startAddr+numRegs-1; // end Register
if (endAddr>49) // end Register can not be more than 49 as we only have record of 50 Registers in total
{
modbusException(ILLEGAL_DATA_ADDRESS); // send an exception
return 0;
}The initial part of this function is same as the other function we saw in the slave programming
- We find the Address of the start Register by using the RxData[2] and [3].
- Then we find the number of Registers requested by the master. This information arrives in RxData[4] and [5].
- As per the standards, the master can write a maximum of 123 Registers at once. So if the master requests more than that, the slave will send an exception regarding ILLEGAL_DTATA_VALUE
- Next we will calculate the the address of the last Register (endAddr). Since I have defined the database for only 50 Registers (0-49), if this end Register address exceeds 49th Register, the slave will send an exception regarding ILLEGAL_DATA_ADDRESS.
If there are no exceptions so far, we will write the data into the database and send the response.
int indx = 7; // we need to keep track of index in RxData
for (int i=0; i<numRegs; i++)
{
Holding_Registers_Database[startAddr++] = (RxData[indx++]<<8)|RxData[indx++];
}
// Prepare Response
//| SLAVE_ID | FUNCTION_CODE | Start Addr | num of Regs | CRC |
//| 1 BYTE | 1 BYTE | 2 BYTE | 2 BYTES | 2 BYTES |
TxData[0] = SLAVE_ID; // slave ID
TxData[1] = RxData[1]; // function code
TxData[2] = RxData[2]; // Start Addr HIGH Byte
TxData[3] = RxData[3]; // Start Addr LOW Byte
TxData[4] = RxData[4]; // num of Regs HIGH Byte
TxData[5] = RxData[5]; // num of Regs LOW Byte
sendData(TxData, 6); // send data... CRC will be calculated in the function itself
return 1; // success
}I am using the indx variable to keep tract of how many bytes of the RxData has been read. Since the actual data starts from the RxData[7], I have defined the indx = 7.
- Here we will combine the 2 bytes of the RxData buffer and store the 16 bit value in the database.
- After each value gets stored, the start address will increment so that the next value can be stored in the next position in the database.
- the indx variable keeps updating, so that we always read the next byte of the RxData buffer.
- The for loop repeats as many times as the number of Registers requested by the master.
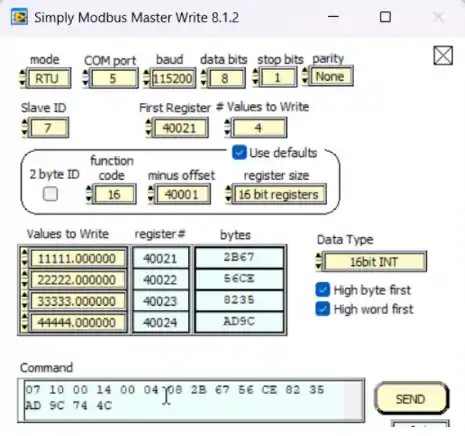
Once the data has been stored, the slave will send a response. The format of the response is shown below.
These are basically the first 6 bytes of the RxData buffer.
So we will copy the individual bytes from RxData into the TxData and send the Response.
Below you can see the query sent by the master software. The master wants to write 4 Registers starting from the 21.
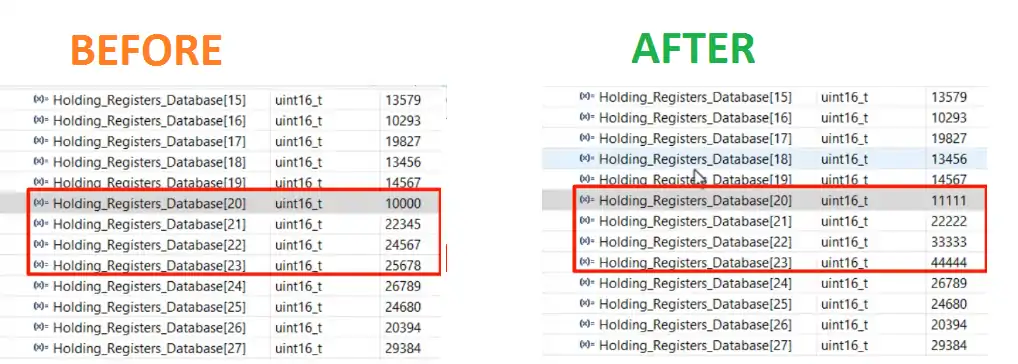
Below is the image showing the Respective registers before and after the query was sent. You can see the value has been updated as per the data sent by the master.
STM32 Modbus RTU Tutorial Series
MODBUS PROTOCOL 101
Modbus #1. STM32 Master Reads Holding and Input Registers
Modbus #2. STM32 Master Reads Coils and inputs
Modbus #3. STM32 Master Writes single Coil and Holding Register
Modbus #3.1 STM32 Master Writes Multiple Coils and Registers
Modbus #4. STM32 as Slave || Read Holding and Input Registers
Modbus #5. STM32 as Slave || Read Coils and Inputs
Info
You can help with the development by DONATING Below.
To download the project, click the DOWNLOAD button.













Hello, I want to ask you if I can map the on-off control of the pins using modbus poll from the computer like having a strip of 8 GPIO pins that I will control the on-off of the pins through the modbus poll software using the corresponding write coil function, how will I map it and how to implement the code. Hope you can help, thank you
If I get it right, the STM32 will act as the slave and the master software wants to control the LEDs via Coils.
To achieve this, check out the PART 7 of this series https://controllerstech.com/modbus-7-stm32-as-slave-writing-coils/
Inside the writeMultiCoils function, after storing the data inside the Coils_Database, you can SET/RESET the LEDs based on it,
/* Update Coils_Database using Modbus data */ int startByte = startAddr / 8; uint16_t bitPosition = startAddr % 8; int indxPosition = 0; int indx = 7; for (int i = 0; i < numCoils; i++) { if (((RxData[indx] >> indxPosition) & 0x01) == 1) Coils_Database[startByte] |= (1 << bitPosition); else Coils_Database[startByte] &= ~(1 << bitPosition); bitPosition++; indxPosition++; if (indxPosition > 7) { indxPosition = 0; indx++; } if (bitPosition > 7) { bitPosition = 0; startByte++; } } // Assume LEDs = coils[0..7] -> GPIOA pins PA0–PA7 uint8_t leds = Coils_Database[0] & 0xFF; GPIOA->ODR = (GPIOA->ODR & ~0xFF) | leds;This line is not supported by Keil.
Holding_Registers_Database[startAddr++] = (RxData[indx++]<<8)|RxData[indx++];
Hello Sir
I am trying to use Modbus to control a servo motor, however, the value does change in the live expressions but the servo motor only reads the value pre written in the register I am reading. Do you have an Idea why?
It should not happen. Try passing the address of the value to the servo as the data inside the memory location do change.
Hey Sir, I have a project where I am using the write register to write a value to control a servo motor, the servo motor does not read the updated values, it only reads the pre-written value in the holding register. However, when I check the live expression of the particular register I’m writing, the value is changing. What could be the problem?