Last Updated: February 5, 2026
Arduino WS2812 LED Interfacing Tutorial (With Full Codes and Cool Animations)
WS2812 LEDs are some of the most popular addressable LEDs used in Arduino projects. These LEDs are bright, colorful, and easy to control. They need only one data pin and can create stunning lighting effects with very little code.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to interface WS2812 LEDs with Arduino using simple steps. We will use an 8-LED circular WS2812 module, which works great for small projects, indicators, wearables, and creative animations.
This guide covers:
- complete wiring
- all important WS2812 functions
- full Arduino codes
- simple explanations
- and several cool animations designed specially for an 8-LED ring

What Are WS2812 LEDs?
WS2812 LEDs are smart RGB LEDs with a built-in controller. This means each LED can show any color, brightness, or animation you want. They use a single data line, so you can control many LEDs using just one Arduino pin.
These LEDs need precise timing, so we usually use a library like Adafruit NeoPixel to make control easy and reliable.
WS2812 LED Features
WS2812 LEDs come with several powerful features:
- Individually addressable: control every LED separately
- Single-wire communication: only one data pin needed
- Built-in driver: no external IC required
- Full 24-bit color: 8-bit Red, Green, and Blue
- Daisy-chain support: connect many LEDs in a series
- High brightness despite low power consumption
These features make WS2812 perfect for rings, strips, matrices, clocks, and wearable LED projects.
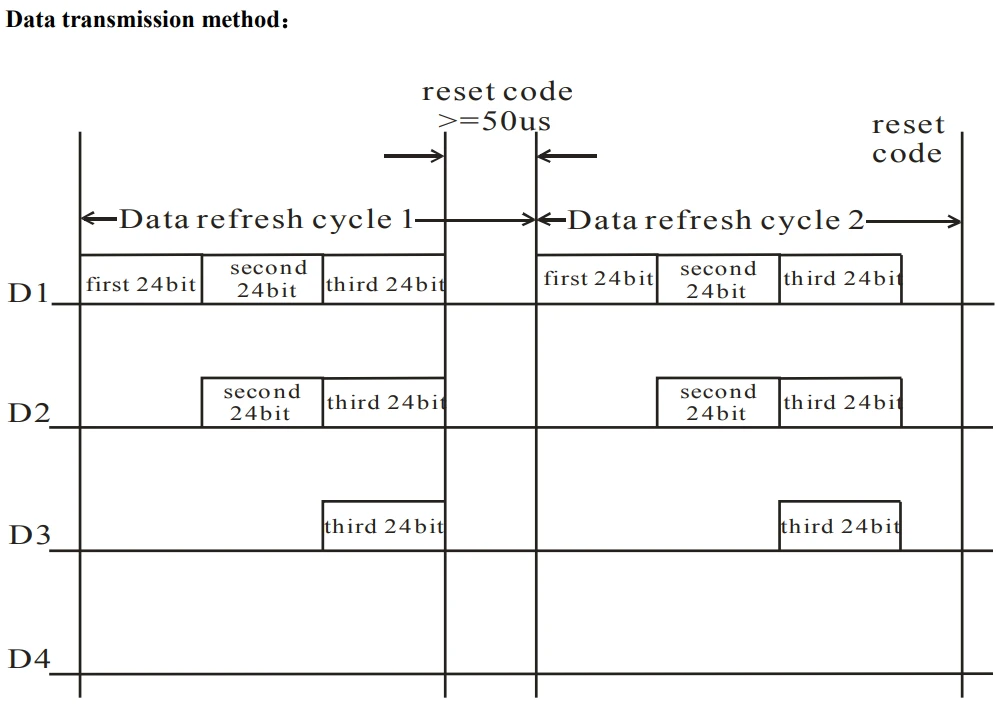
How WS2812 Data Signal Works
WS2812 LEDs communicate using a special timing-based protocol:
- Arduino sends a fast stream of 1s and 0s
- Each bit has a different pulse width
- The LED interprets those bits as color values
- After receiving 24 bits (RGB), the LED updates itself
- Then it passes the remaining data to the next LED in the chain
Because the timing is very strict, writing code manually is difficult. This is why we use the NeoPixel library, it handles all timing and color data automatically.
Setting Up WS2812 LEDs with Arduino
To control WS2812 LEDs easily, we will use the Adafruit NeoPixel library. This library handles all the complex timing and data signals automatically. It lets us set colors, brightness, and animations with simple functions.
In this section, you will install the library, make the basic wiring, and run your first WS2812 LED test.
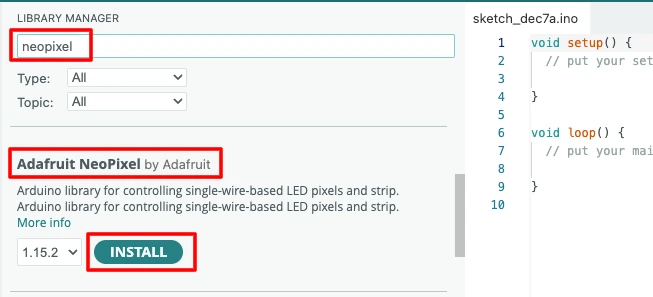
Install Adafruit NeoPixel Library
Follow these steps to install the library in Arduino IDE:
- Open Arduino IDE
- Go to Sketch → Include Library → Manage Libraries
- In the search box, type “NeoPixel”
- Select Adafruit NeoPixel
- Click Install
Once installed, you can use all WS2812 functions without worrying about timing issues.
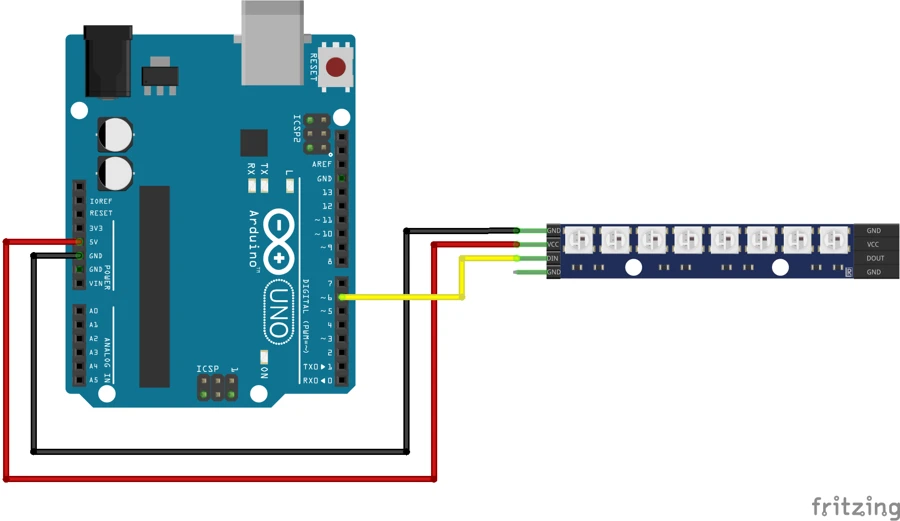
Circuit Diagram for Arduino + 8-LED WS2812 Ring
The wiring is very simple. The 8-LED NeoPixel ring has three pins:
- 5V -> Arduino 5V
- GND -> Arduino GND
- DIN -> Arduino Digital Pin 6
Recommended Safety Components:
- A 470 Ω resistor between Arduino pin 6 and DIN
- A 1000 µF capacitor across 5V and GND
- Use an external 5V supply for long strips (not required for 8 LEDs)
Basic Arduino Test Code (Turn All LEDs On)
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin(); // Initialize the LED ring
ring.show(); // Turn off all LEDs initially
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < LED_COUNT; i++) {
ring.setPixelColor(i, ring.Color(255, 0, 0)); // Set each LED to red
}
ring.show(); // Update the ring to apply color
}Explanation
ring.begin()initializes the WS2812 ring.ring.setPixelColor()sets the color of each LED.ring.show()sends the data signal to the LEDs.- The loop turns all 8 LEDs red.
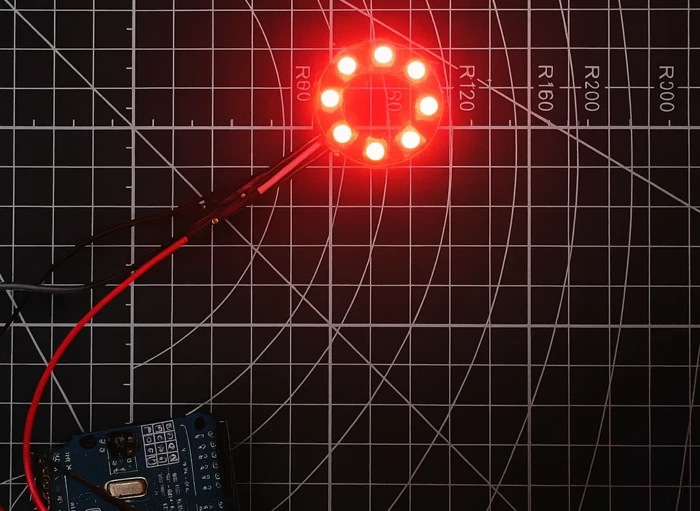
Output
The image below shows all 8 LEDs glowing in solid red color on the WS2812 ring.
WS2812 LED Functions in Arduino
In this section, we will cover all must-know WS2812 functions one by one. These functions help you control colors, brightness, clearing, and updating the LEDs.
Set Pixel Color (Single LED Control)
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
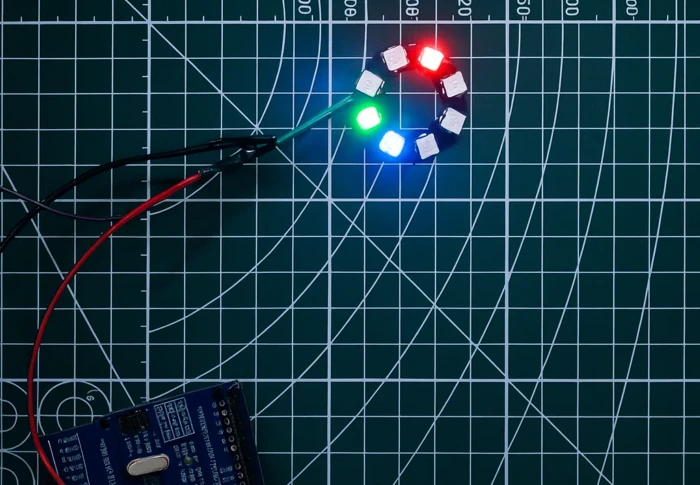
ring.setPixelColor(0, ring.Color(0, 255, 0)); // LED 0 → Green
ring.setPixelColor(3, ring.Color(255, 0, 0)); // LED 3 → Red
ring.setPixelColor(7, ring.Color(0, 0, 255)); // LED 7 → Blue
ring.show(); // Apply changes
}
Explanation
setPixelColor(0, ...)sets LED number 0 to a selected color.- You can choose any LED index from 0 to 7.
- Each color uses Red, Green, Blue values.
Output
The image below shows LEDs 0, 3, and 7 glowing in green, red, and blue respectively.
Fill All LEDs with One Color
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
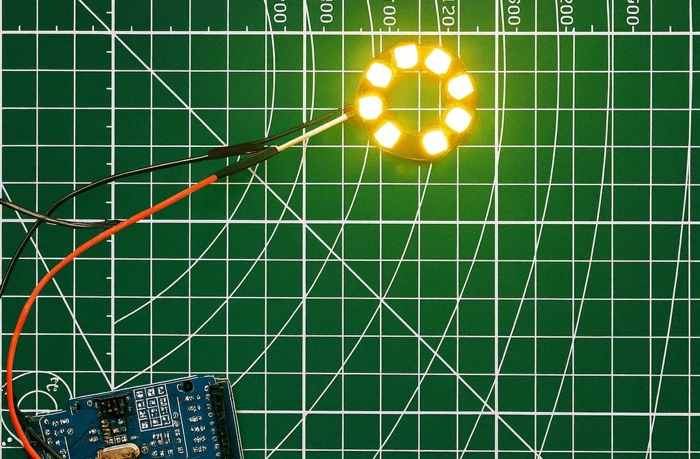
ring.fill(ring.Color(255, 255, 0)); // Fill all LEDs with yellow
ring.show();
}
Explanation
ring.fill(color)sets every LED to the same color.- The example fills all LEDs with yellow (255 red + 255 green).
Output
The image below shows all 8 LEDs glowing in bright yellow.
Set Brightness of WS2812 LEDs
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
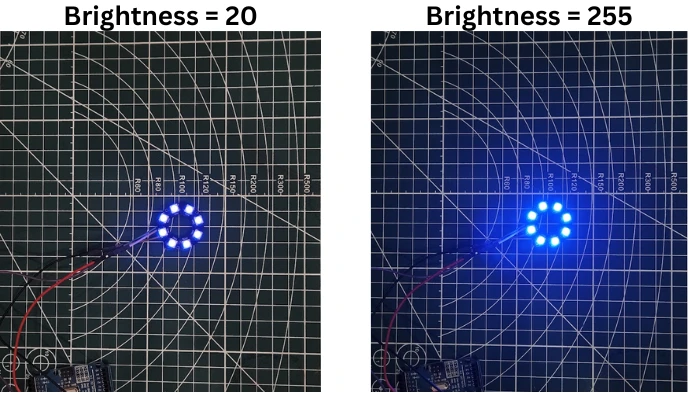
ring.setBrightness(20); // Brightness range: 0 to 255
// ring.setBrightness(255); // Brightness range: 0 to 255
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
ring.fill(ring.Color(0, 0, 255)); // Blue
ring.show();
}Explanation
setBrightness(value)changes brightness from 0 (dim) to 255 (full).ring.fill()fills all the LEDs with blue color.
Output
The image below shows the difference in brightness for all LEDs, when the brightness is set to 20 vs 255.
Clear LEDs
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
ring.fill(ring.Color(255, 0, 0)); // Red
ring.show();
delay(1000);
ring.clear(); // Clear all LEDs
ring.show();
delay(1000);
}Explanation
ring.clear()resets all LEDs to off.- You must call
ring.show()to apply the change.
Output
The gif below shows LEDs glowing red for 1 second, then turning off.
Useful WS2812 Effects (Easy Mini Animations)
In this section, we will create common and simple WS2812 LED effects. These animations are perfect for beginners because they use basic functions but still look attractive.
Breathing Effect
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
for (int brightness = 0; brightness <= 255; brightness++) {
ring.setBrightness(brightness);
ring.fill(ring.Color(0, 0, 255)); // Blue
ring.show();
delay(5);
}
for (int brightness = 255; brightness >= 0; brightness--) {
ring.setBrightness(brightness);
ring.fill(ring.Color(0, 0, 255)); // Blue
ring.show();
delay(5);
}
}Explanation
- Brightness slowly increases and decreases.
- Creates a breathing or pulsing glow.
- We apply the same color on each cycle.
Output
The gif below shows the LEDs glowing blue with a soft fade-in and fade-out breathing effect.
Color Wipe Animation
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < LED_COUNT; i++) {
ring.setPixelColor(i, ring.Color(0, 255, 0)); // Green wipe
ring.show();
delay(120);
}
delay(500);
ring.clear();
ring.show();
delay(300);
}Explanation
- LEDs turn on one by one in the same color.
- Looks like the color is wiping across the ring.
- Example uses green for a smooth wipe effect.
Output
The gif below shows a green color wiping across the ring and then clearing.
Best Cool Animations for WS2812 Ring (8-LED NeoPixel Ring)
These animations are optimized for a circular 8-LED WS2812 module. They look smooth, colorful, and visually pleasing because they naturally follow the circular shape of the ring.
Clockwise Rotation Effect
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
static int pos = 0;
ring.clear();
ring.setPixelColor(pos, ring.Color(255, 100, 0)); // Orange
ring.show();
pos++;
if (pos >= LED_COUNT) pos = 0;
delay(120);
}Explanation
- Only one LED stays ON at a time.
- Position increases from 0 to 7, creating a clockwise movement.
- Uses warm orange color for a glowing rotating effect.
Output
The gif below shows a single orange LED smoothly rotating clockwise around the ring.
Counter-Clockwise Rotation
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
static int pos = 7; // Start from the last LED
ring.clear();
ring.setPixelColor(pos, ring.Color(0, 200, 255)); // Cyan
ring.show();
pos--;
if (pos < 0) pos = LED_COUNT - 1;
delay(120);
}Explanation
- Index moves backward from 7 to 0.
- Creates a clean counter-clockwise effect.
- Color set to cool cyan.
Output
The gif below shows a cyan LED rotating counter-clockwise around the ring.
Fire-Ring Effect (Warm Flickering Colors)
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
}
void loop() {
for (int i = 0; i < LED_COUNT; i++) {
int intensity = random(150, 255); // Flicker brightness
ring.setPixelColor(i, ring.Color(intensity, random(40, 80), 0));
}
ring.show();
delay(80);
}Explanation
- Random brightness + warm tones (red/orange/yellow).
- Creates a natural flickering flame effect.
- Updates quickly for a real fire-like animation.
Output
The gif below shows warm fire-like flickers moving around the ring.
Dual-Color Opposite Rotation
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
}
void loop() {
static int pos1 = 0;
static int pos2 = 4; // Opposite LED
ring.clear();
ring.setPixelColor(pos1, ring.Color(255, 0, 0)); // Red
ring.setPixelColor(pos2, ring.Color(0, 0, 255)); // Blue
ring.show();
pos1++;
pos2--;
if (pos1 >= LED_COUNT) pos1 = 0;
if (pos2 < 0) pos2 = LED_COUNT - 1;
delay(150);
}Explanation
- Two LEDs rotate in opposite directions.
- Colors: red clockwise, blue counter-clockwise.
- Creates a symmetrical dual-rotation effect.
Output
The gif below shows two LEDs rotating in opposite directions with red and blue colors.
Sparkle Effect for 8-LED Ring
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
}
void loop() {
ring.clear();
int randomLED = random(0, LED_COUNT);
ring.setPixelColor(randomLED, ring.Color(255, 255, 255)); // White sparkle
ring.show();
delay(80);
}Explanation
- Random LED lights up in white.
- Looks like small sparkles or twinkling stars.
- Works great on circular rings and small displays.
Output
The gif below shows random white sparkles appearing across the LED ring.
WS2812 Rainbow Effects
In this section, we’ll explore how to create vibrant and dynamic rainbow animations for the WS2812 ring. These effects cycle smoothly through multiple colors, making the ring look far more lively and visually appealing.
Rotating rainbow effect
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 6
#define NUM_LEDS 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
rainbowEffect(20); // Lower = faster rainbow
}
// Smooth rainbow wheel
void rainbowEffect(uint8_t wait) {
for (long firstPixelHue = 0; firstPixelHue < 5 * 65536; firstPixelHue += 256) {
for (int i = 0; i < ring.numPixels(); i++) {
int pixelHue = firstPixelHue + (i * 65536L / ring.numPixels());
ring.setPixelColor(i, ring.gamma32(ring.ColorHSV(pixelHue)));
}
ring.show();
delay(wait);
}
}Explanation
This code creates a smooth rainbow animation by changing the hue value of each LED. The function rainbowEffect() continuously shifts the color wheel and updates all 8 LEDs. Each LED gets a slightly shifted hue, which makes it look like the rainbow is moving around the ring.
The line ring.ColorHSV() generates natural rainbow colors, and gamma32() makes the colors look smoother to the human eye. The animation speed is controlled by the wait delay.
Output
The gif below shows the rotating rainbow effect on the WS2812 LED ring.
Rainbow Breathing Pulse
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
#define PIN 6
#define NUM_LEDS 8
Adafruit_NeoPixel ring(NUM_LEDS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
void setup() {
ring.begin();
ring.show();
}
void loop() {
rainbowBreathing(10);
}
void rainbowBreathing(uint8_t wait) {
static uint16_t hueBase = 0;
hueBase += 20; // rainbow shift
// Smooth breathing brightness: 0 → 255 → 0
float breathe = (exp(sin(millis() / 1000.0 * PI)) - 0.36787944) * 108.0;
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
uint16_t hue = hueBase + (i * 65536L / NUM_LEDS);
uint32_t color = ring.ColorHSV(hue, 255, (uint8_t)breathe);
ring.setPixelColor(i, ring.gamma32(color));
}
ring.show();
delay(wait);
}Explanation
- All LEDs show a shifting rainbow, but the brightness fades in and out smoothly.
- The breathing pattern is created using a sine-based brightness curve.
- The rainbow shifts continuously, giving a soft glowing pulse.
Output
The gif below shows the rainbow breathing effect on the WS2812 LED ring.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we covered everything you need to start working with WS2812 LEDs using Arduino. You learned the basics of how WS2812 works, how to wire an 8-LED NeoPixel ring, and how to use essential functions like setting colors, adjusting brightness, clearing LEDs, and showing updates. We also explored useful effects and advanced animations, including rainbow spin, two-direction rotation, sparkles, and breathing pulses.
These examples help you understand how flexible and powerful WS2812 LEDs can be. With just one data pin and a few lines of code, you can create stunning light patterns for hobby projects, indicators, clocks, or decorative lighting. You can now mix these effects, modify colors, and build your own animations to make your projects look more creative and professional.
Browse More Arduino Display Tutorials
How to Interface GP2Y0A41SK0F Distance Sensor with Arduino (Serial Monitor + I2C LCD Display)
Arduino DS18B20 Temperature Sensor Tutorial: Single and Multiple Sensors with SSD1306 OLED
IR Sensor Arduino Tutorial: Interfacing, Calibration, Detection Modes, Codes & LCD1602 Display
HC-SR04 Arduino Tutorial: Measure Distance and Display on Serial Monitor & LCD1602 I2C
Interface AHT20 Sensor with Arduino | Measure Temperature and Humidity with OLED Display
ADXL345 Arduino I2C Tutorial: Pinout, Wiring, Calibration, and Accelerometer Data Reading Explained
Interface DHT11 and DHT22 with Arduino | Temperature and Humidity Sensor Tutorial
Arduino WS2812 Project Download
Info
You can help with the development by DONATING Below.
To download the project, click the DOWNLOAD button.
Arduino WS2812 FAQs
Flickering usually happens due to unstable power. Use a common ground and add a small capacitor (like 1000 µF) across the LED power lines.
Yes, but it’s harder. You would need precise timing code. Using NeoPixel or FastLED is recommended to avoid timing issues.
Only a few. For larger LED strips, use an external 5V supply with enough current, and connect ground to Arduino.
Use a level shifter (5V data) for better signal stability, especially when using long LED chains.
Yes. Create separate functions for each animation and call them in sequence or based on a timer to switch effects.