Interface ADXL345 Accelerometer with STM32
The ADXL345 is a complete 3-axis acceleration measurement system with a selectable measurement range of ±2 g, ±4 g, ±8 g, or ±16 g. It measures both dynamic acceleration resulting from motion or shock and static acceleration, such as gravity, which allows the device to be used as a tilt sensor. In this tutorial we are going to interface ADXL345 with STM32 using I2C.
ADXL345 can be used for a whole bunch of things for eg-
- To measure acceleration in three axis
- To measure Roll and Pitch
- To measure single or double tap etc..
Today in this tutorial, we will only cover the measurement of acceleration in three axis. And rest of them will be covered in the near future.
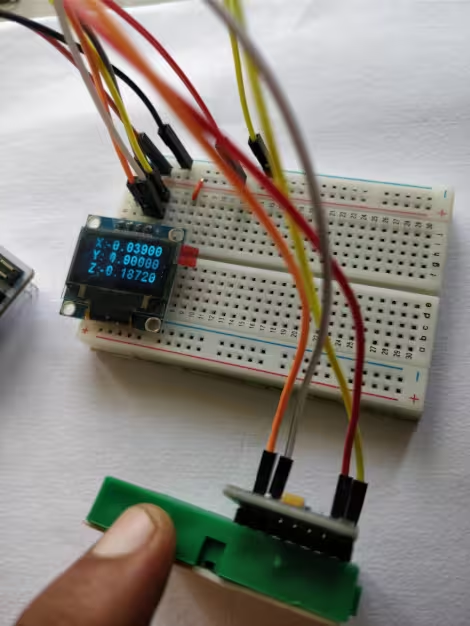
We will display the Acceleration data on the 0.96″ Oled screen. I have already covered how to interface the SSD1306 Oled display with STM32 using the I2C. Here we are going to connect both, the Display and the Sensor, to the same I2C.
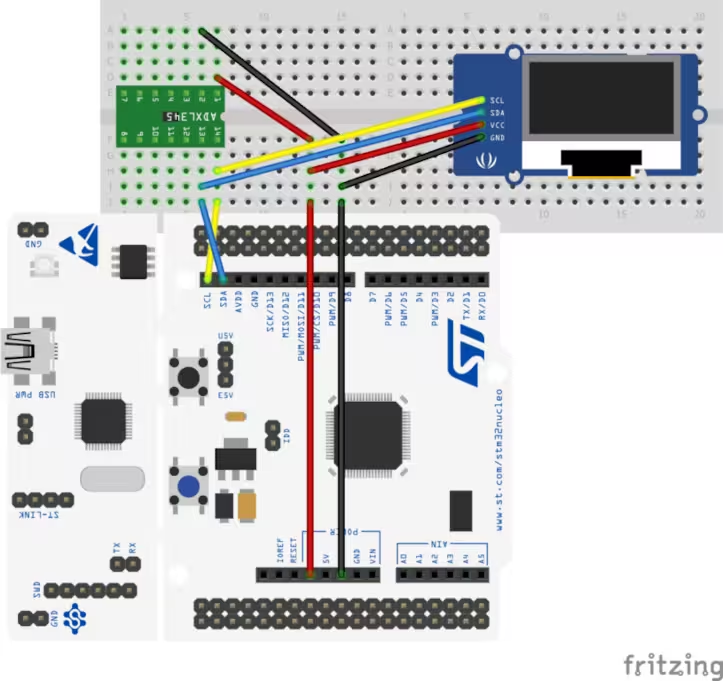
Connection
As you can see in the image above, the Oled display and the sensor both are connected using the same I2C pins. Also both of them are powered by the 3.3V from the board itself.
CubeMX Configuration
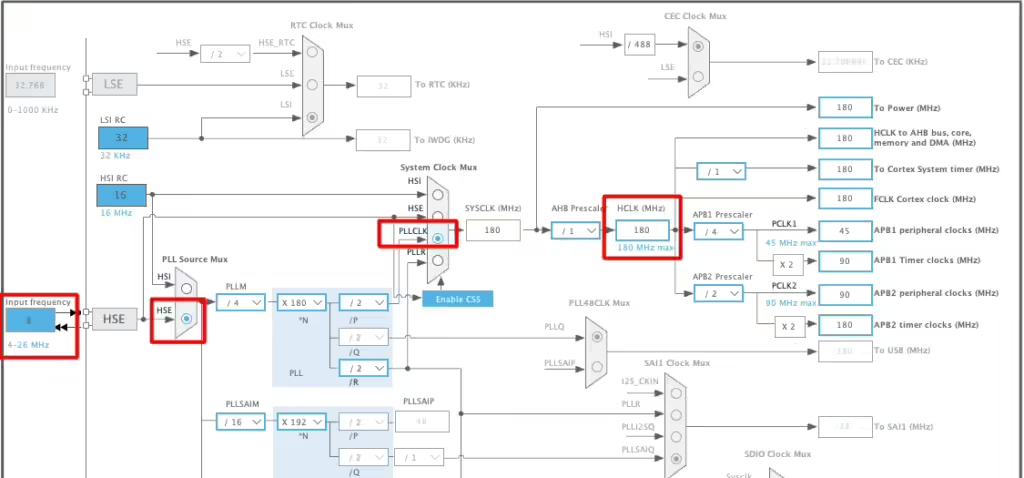
Below is the image showing the Clock configuration for this project.
I have enabled the External Crystal to provide the clock. The Nucleo F446RE has 8MHz crystal on board and we will use the PLL to run the system at maximum 180MHz.
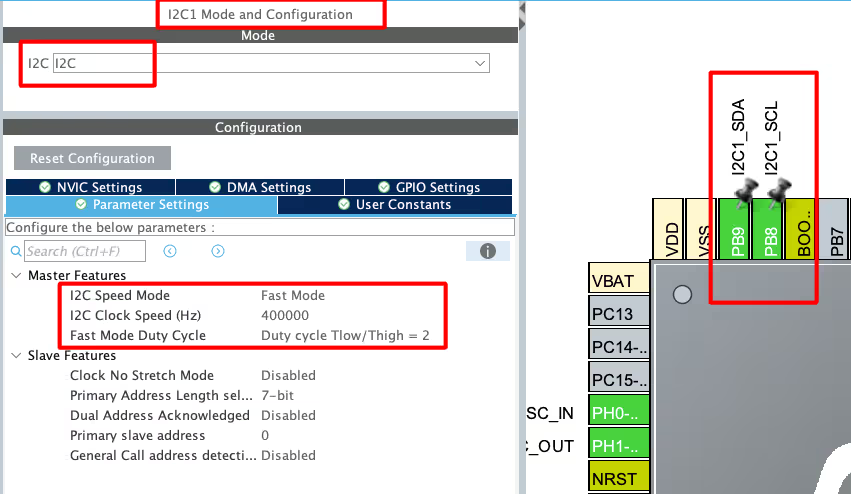
Below is the image showing the I2C configuration.
I am using I2C1 to connect both, Display and sensor. The I2C is configured in the FAST MODE with the clock speed of 400KHz. Also the pins PB8 and PB9 are configured as the SCL and SDA pins.
The CODE
#define ADXL_Address 0x53<<1
uint8_t RxData[10];
float xg, yg, zg;First we will define an array to store the data received from the sensor. Also define the float variables to store the converted data in the g form.
As per the datasheet, the slave Address of the ADXL345 is 0xA6. This is the write address of the device and the HAL library will take care of the read address by itself.
INITIALIZATION
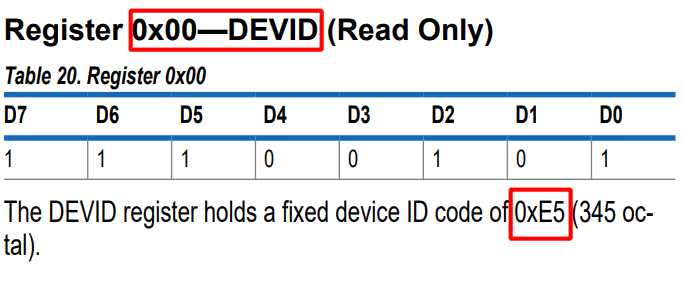
We will first check if the slave device is responding, by reading the ID Register (0x00). The ADXL should respond with the value 0xE5.
void ADXL_Init (void)
{
uint8_t chipID=0;
ADXL_Read(0x00, &chipID, 1);If the DEV_ID returned is 0xE5, we will proceed with the initialisation.
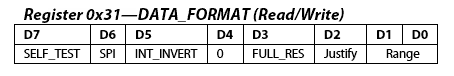
Here we will modify POWER_CTL Register (0x2D) and DATA_FORMAT Register (0x31).
First RESET all bits of POWER_CTL register by writing 0 to them.
if (chipID == 0xE5)
{
ADXL_Write_Reg (0x2d, 0x00); // reset all bits; standby
ADXL_Write_Reg (0x2d, 0x08); // measure=1 and wake up 8hzNext SET the MEASURE bit, RESET the SLEEP bit and SET the frequency in the WAKE UP bits
Next, in the DATA_FORMAT Register, Set the RANGE using D0 and D1.
ADXL_Write_Reg (0x31, 0x01); // 10bit data, range= +- 4g
}
}The main function
Inside the main function, we will first initialise the Oled and the ADXL.
int main()
{
....
SSD1306_Init(); // initialize OLED display
SSD1306_GotoXY (1, 1);
SSD1306_Puts ("Initializing...", &Font_11x18, 1);
SSD1306_UpdateScreen (); // update display
ADXL_Init(); // initialize adxl
SSD1306_Clear();We will write the rest of the code in the while loop.
while (1)
{
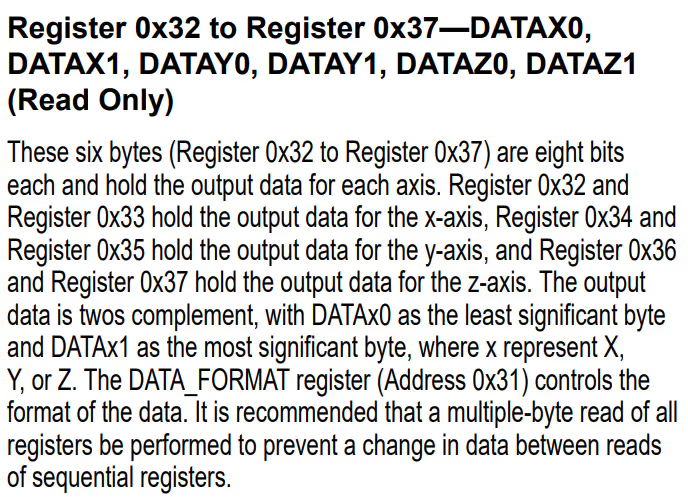
ADXL_Read(0x32, RxData, 6);Here we will first read 6 bytes starting from the Register 0x32. The data is stored in the Registers 0x32 to 0x37 in the form of DATA X0, DATA X1, DATA Y0, DATA Y1, DATA Z0, DATA Z1.
Now we need to combine the DATA X0, DATA X1 into single 10 bit value and this can be done by
int16_t RAWX = ((RxData[1]<<8)|RxData[0]);
int16_t RAWY = ((RxData[3]<<8)|RxData[2]);
int16_t RAWZ = ((RxData[5]<<8)|RxData[4]);Next we will convert this data into the g form in order to check for the acceleration in specific axis. As you can check above in the initialisation part, we have set the range of ±4 g. According to the datasheet, for the range of ±4 g, the sensitivity is 128LSB/g.
So to convert into g, we need to divide the value by 128.
xg = (float)RAWX/128;
yg = (float)RAWY/128;
zg = (float)RAWZ/128;Now we can display this data on the display. We will call the function display_data to display the float value on the oled. This function is explained below.
SSD1306_GotoXY (16, 1);
SSD1306_Puts ("X: ", &Font_11x18, 1);
SSD1306_GotoXY (32, 1);
display_data (xg);
SSD1306_GotoXY (16, 20);
SSD1306_Puts ("Y: ", &Font_11x18, 1);
SSD1306_GotoXY (32, 20);
display_data (yg);
SSD1306_GotoXY (16, 40);
SSD1306_Puts ("Z: ", &Font_11x18, 1);
SSD1306_GotoXY (32, 40);
display_data (zg);
HAL_Delay (500);
}
}Here we are displaying the data for all three axis in different rows.
Below is the function display_data.
void display_data (float data)
{
char axischar[5];
sprintf (axischar, "%.2f", data);
SSD1306_Puts (axischar, &Font_11x18, 1);
SSD1306_UpdateScreen (); // update display
}Here we will first convert the float data into the ascii format and then send the converted array to the display.






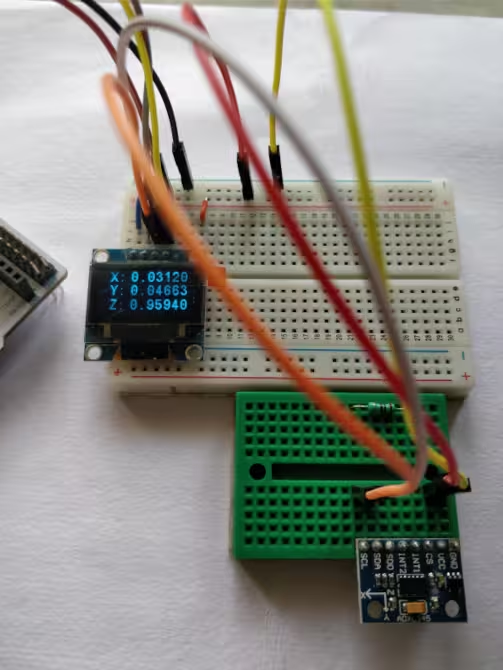
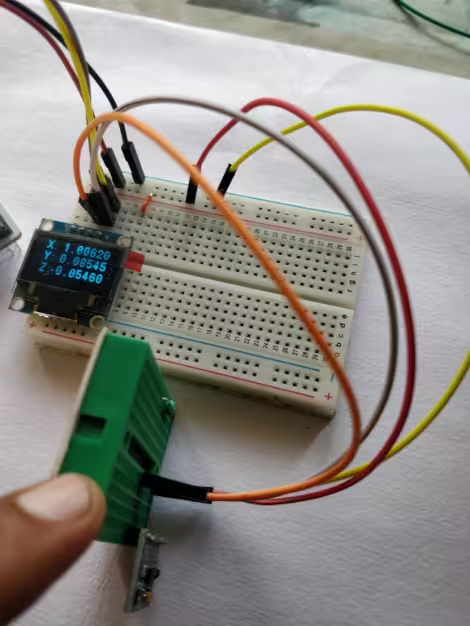
The reason why you are getting 65535 value; the hex value of -1 in signed int16_t form is 0xFFFF. However, if you store it in the uint16_t variable, it will be read as 65535. I am assuming that the default acceleration value at rest is -1g.
stm32 – How to read data from MPU6050 using STM32F4 – Stack Overflow
@Anil
Hi,
How to initialise the LIS3DH sensor?
You have not enabled the sleep mode (SLEEP bit is 0) so measure and wakeup at 8Hz is of no use. The data rates can be set by ‘Register 0x2C—BW_RATE’. Am I right?
Hello, I m follow above step but my end ADXL345 sensor given 65535 output value…how to resolve these problem…
follow this, it will help you resolve it, https://www.engineersgarage.com/adxl345-accelerometer-arduino-i2c/
it’s for arduino, but just focus on how he did the formatting of data
DONATE and DOWNLOAD links don’t work.
It’s fixed now.. Thanks for informing
sorry for too much specific question, in general what would you have searched in case you need to make freefall example for your sensor in application notes or datasheet
freefall means the “g” value will change. The acceleration of the free fall (If you know basic physics)
anyone know free-fall example for lis3dsh on accelerator by following ST application notes (doc no. AN3393) section 9.3. free-fall but couldn’t get the interrupt for free fall
hi.how can i show ADC value on the oled lcd?